This section covers the following topics:
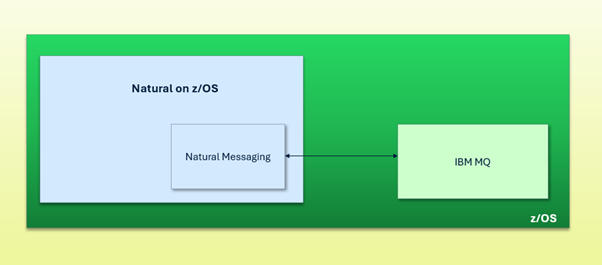
Natural Messaging allows for direct integration with messaging systems, enabling Natural users to easily exchange data.
All interactions with IBM MQ are handled through the Natural Messaging interface.
The PROCESS statement is
used to put messages on queues or retrieve them.
The FIND statement is used to
browse queues.
Natural Messaging enables Natural on z/OS to seamlessly send and receive messages via IBM MQ, enabling smooth integration with other MQ-based systems and applications.
The Natural interface for messaging consists of the following components:
The NMQNUC module, which is mandatory, environment-independent, and
delivered as a load module only. This module is linked to the shared nucleus.
The NMQTAB module, which is also mandatory and delivered as a load
module only. This module is linked to the frontend.
DDMs for MQ access, which are delivered with the NMQ INPL file.
Natural Messaging provides seamless integration with IBM MQ, enabling Natural applications to send and receive messages via MQ queues. It is suitable for high-performance transactional applications running in z/OS environments.
Natural Messaging operates in the following environments:
Com-plete
CICS
Batch
TSO
Note
Under CICS, Natural Messaging integrates with IBM MQ via the MQ Adapter
for CICS. Both conversational and pseudo-conversational modes are supported.
This section covers the following topics:
Natural Messaging can access the following MQ object types:
Local queues
Natural Messaging supports both persistent and non-persistent messages, and can process messages in FIFO (First In First Out) or priority-based order depending on the queue configuration.
Natural Messaging supports:
GET with WAIT and NOWAIT options.
Browsing (read and keep message) and destructive GET (read and remove
message).
CorrelId- and MsgId-based filtering.
Natural Messaging is optimized for high-performance messaging via:
Connection reuse across MQ calls.
Object handle reuse wherever possible.
Efficient memory usage for message buffers.
Queue open and close operations are minimized through pooling.
For Natural Messaging to interface with IBM MQ, the environment-dependent nucleus for each runtime environment must be linked with the following modules:
NMQTAB (Natural Messaging interface configuration table)
IBM MQ stub program (specific to the environment)
IBM MQ stub programs by environment:
| Environment | Required IBM MQ Stub Program |
|---|---|
| Com-plete | CSQBSTUB (batch MQ stub program) |
| CICS | CSQCSTUB (CICS MQ stub program) |
| TSO | CSQBSTUB (batch MQ stub program) |
| Batch | CSQBSTUB (batch MQ stub program) |
For detailed installation instructions, see Installing Natural Messaging in the Installation for z/OS documentation.
Task affinity is required in Com-plete during MQ operations (such as the execution of
the PROCESS statement or within a FIND loop) to ensure correct
execution. This is because MQ internally relies on the same task context to maintain
consistency between requests and completions.
In Natural Messaging under Com-plete, task affinity is forced internally during MQ call operations.
When using MQ with Com-plete, configure a sufficient number of tasks to accommodate affinity requirements and avoid system slowdowns.
PUT and GET operations are performed immediately. They become
permanent and cannot be rolled back.
The following runtime conditions must be met when using Natural Messaging under CICS:
The CICS region must be connected to a queue manager through the MQ CICS adapter before any messaging operations can be performed.
Transactional behavior: In the current version - particularly in CICS environments
- PUT and GET operations are performed with a
SYNCPOINT, making them transactional.
Message operations are committed under the following circumstances:
Upon a terminal I/O in a pseudo conversation session where the
end-of-transaction results in a SYNCPOINT commit.
By means of the END
TRANSACTION statement. To use this option, you must set the
parameter ETSYNC=ON.
At the end of the session.
There are no additional environment-specific considerations beyond the standard linking and runtime requirements, which are similar to those in other environments.
PUT and GET operations are performed immediately. They become
permanent and cannot be rolled back.
When Natural Messaging runs under Natural Development Server (NDV) with
SECURITY_MODE=IMPERSONATE_LOCAL, the NDV session executes under the local
identity of the NaturalONE client user. In this mode, the MQ adapter must load within a
stable user security context.
If the NDV server runs with SECURITY_CACHING=NO, the impersonation token
is recreated for each request. This causes the MQ adapter to fail with NMQ2129
MQRC_ADAPTER_CONN_LOAD_ERROR. Therefore,
SECURITY_CACHING=YES is required when SECURITY_MODE is set
to IMPERSONATE_LOCAL to ensure consistent adapter loading and successful MQ
connection establishment.
This section covers runtime behaviors across all supported environments (Batch, TSO, CICS, and Com-plete).
When a BROWSE operation is performed, an implicit internal commit is
automatically triggered by Natural before executing the BROWSE, except in
the CICS environment..
The message retrieved from or written to an MQ queue is held in one of the internal buffers managed by Natural Messaging. Therefore, ensure that the Natural thread size is configured sufficiently to accommodate the size of the message being processed.
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| MQ | MQ refers to IBM's MQ for z/OS. |
| DDM | Data definition module. |
| NMQ | This is the product code of Natural Messaging. In this documentation, the product code is often used as prefix in the names of data sets, modules, etc. |