This document covers the following topics:
When you start the Natural Web I/O Interface client in the browser, a logon page appears. The entries in this logon page depend on the settings in your Session Configuration.
In order to start a Natural application from the logon page, you enter the following URL inside your browser:
http://<host>:<port>/natuniweb/natural.jsp
where <host> and <port> are the host name and port number of your application server.
For each session definition that has been configured in the configuration file, an entry appears on the logon page. If the user selects the corresponding entry, only those parameters that were not pre-configured in the configuration file need to be specified in the logon page in order to start the application. Usually, you will preconfigure all connection parameters except user name and password.
The following example shows part of a logon page which results from a configuration file in which no special entries are defined for a session:
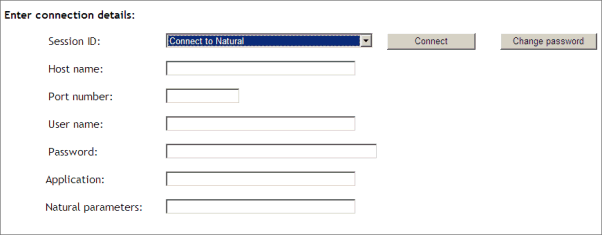
The following example shows part of a logon page which results from a configuration file in which many settings are already predefined (including user ID and password):

To log on to a session, you have to specify all required information in the logon page (for example, you select a session from the corresponding drop-down list box). When you choose the button, the screen for the selected session appears.
The following description applies if you want to switch to a different CICS transaction on a mainframe. It is also possible to select a different host and port number.
You specify the dynamic server parameters in the same text box in which you also specify the dynamic parameters for the Natural environment. So that the dynamic server parameters can be evaluated, it is important that you specify it before any Natural parameters, using the following syntax:
<TA_NAME=name TA_HOST=hostname TA_PORT=number>
- name
Can be 1 to 4 characters long. This must be the name of an existing CICS transaction which applies to a CICS Adapter. It will override the transaction name, currently defined in the configuration file for the CICS Adapter on the Natural Web I/O Interface server (NWO). Ask your administrator for further information.
- hostname
Can be 1 to 32 characters long. This must be the name, or the TCP/IP address of the host the desired CICS is running. It will override the hostname (RFE_CICS_TA_HOST), currently defined in the configuration file for the CICS Adapter on the Natural Web I/O Interface server (NWO). Ask your administrator for further information.
- number
Can be a numeric value in the range from 1 to 65535. It is the TCP/IP port of the CICS-supplied listener. It will override the hostname (RFE_CICS_TA_PORT), currently defined in the configuration file for the CICS Adapter on the Natural Web I/O Interface server (NWO). Ask your administrator for further information.
Make sure to put the entire definition in angle brackets. Dynamic server parameters can be separated by a comma or a blank character. Only the parameters to be overwritten must be specified. When this definition is followed by a Natural parameter, insert a blank before the Natural parameter.
<TA_NAME=NA82 TA_HOST=HOST.LOCAL.NET TA_PORT=1898> STACK=(LOGON SYSCP)
If one of the dynamic server parameters is incorrect, an error message occurs, and the session cannot be started.
If an incorrect CICS transaction id is specified, the error message EZY1315E
09/03/24 15:17:46 INVALID TRANID=G PARTNER INET ADDR=ip-address occurs.
If an incorrect hostname or port number is specified, the error message NAT9939
Open socket connection failed occurs.
Note
The above definition of dynamic server parameters can also be specified in the
configuration tool, in the same place
where you also specify the Natural parameters, and together with the URL parameter
natparam .
The following information applies when the field for entering a password appears on the logon page. This field does not appear when a password has already been defined in the configuration file.
Under Windows and Linux, you always have to enter the operating system password, even if Natural Security is active.
On the mainframe, this is different: When Natural Security is not active, you have to enter the operating system password. When Natural Security is active, you have to enter the Natural Security password.
Currently, this functionality is only available for Natural for Linux and Natural for Windows.
The following information applies when the fields for entering a user ID and a password appear on the logon page. These fields do not appear when user ID and password have already been defined in the configuration file; in this case, it is not possible to change the password in the logon page.
When your password has expired, you are automatically asked for a new password. When you try to log on with your current password, an error message appears and input fields for changing the password are shown.
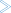 To change the password
To change the password
Choose the button in the logon page.
The name of this button changes to Don’t change password and the following two input fields are shown in the logon page:
New password
Repeat new password
Enter your user ID and your current password as usual.
Enter the new password in the two input fields.
Choose the button to change the password.
Or:
If you do not want to change your password, choose the Don’t change
password button. The two input fields will then disappear.
The browser's "Back" and "Forward" buttons do not work with the Natural Web I/O Interface client and should therefore not be used.
If you want to run two Natural sessions in parallel, you have to start a new instance of the browser (for example, by choosing the corresponding icon in the Quick Launch toolbar of Windows). You must not use the browser's "New Window" function. This would result in one session running in two browsers, which is not allowed.