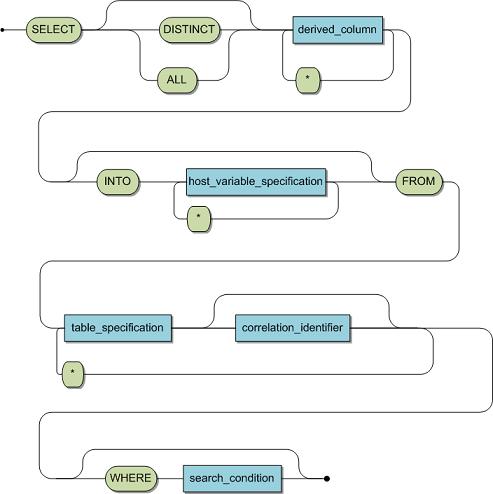
SELECT (SINGLE ROW)
Function
The single row SELECT statement obtains a single row of data from the database according to the specified conditions.
Invocation
Embedded Mode P Dynamic Mode Interactive Mode
Syntax
Elements which are also part of the query specification are described in detail in User Reference Guide > SQL Grammar > SQL Language Elements > Query Specification in the Adabas SQL Gateway User Guide.
derived_column | The corresponding columns in the final resultant table that is derived by the query. Derived columns are separated by commas and all of them together are referred to as the derived column list. |
* | An abbreviated form of listing all derived columns of all tables in the table name list. In ANSI compatibility mode, it is not permitted to qualify the asterisk by using the correlation identifier or the table specification. |
host_variable_specification | A single host variable. Only relevant for (INTO clause) single row SELECT. The host variables are intended to receive the returned data as specified by the SELECT statement's derived column list. |
table_specification | A table specification, as described in the User Reference Guide > SQL Grammar > SQL Language Elements > Table Specification section of this documentation. |
correlation_identifier | Alternative name for a particular table for use within the query and subqueries which are in scope. |
WHERE clause | Search condition which candidate rows must fulfill in order to become part of the resultant table. |
Description
The single row SELECT statement is used to obtain a single row of data from the database.
The single row SELECT statement can only be embedded and can only return one or no rows. A negative error code is returned in the sqlcode field of the SQLCA, if the resultant table actually contains more than one row. This is because the specified host variables in the INTO clause can only receive one row of data. A host variable specification which references a host variable structure is equivalent to individual host variable specifications which reference all the elements of a structure one by one.
The single row SELECT statement is the only invocation of a SELECT statement where an INTO clause is allowed and required. The only other way to specify an INTO clause is as a part of the FETCH statement. For details, please refer to the
FETCH statement section.
Limitations
A maximum of one row can be returned. The use of a valid INTO clause is required.
ANSI Specifics
None.
CONNX Embedded SQL Specifics
DML statements must not be mixed with DDL/DCL statements in the same transaction.
Here is an example that determines how many people can be accomodated in the 6230 yacht:
SELECT bunks
INTO :bunks
FROM yacht
WHERE yacht_identifier = 6230;