About the Apama event stream processing model
The Apama event stream processing model consists of a network of streams and processing nodes; a processing node whose logic is expressed in terms of a relational query expression is a stream query.
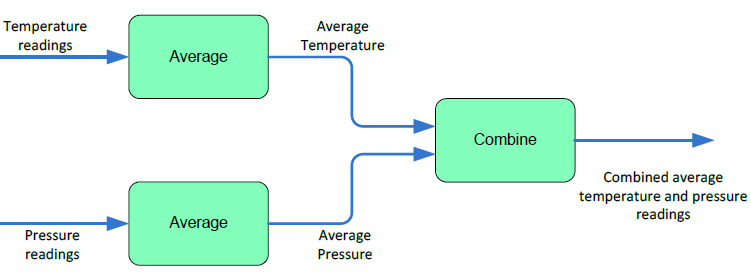
The diagram below shows an example of a stream processing network.
The network consists of five streams1 and three stream queries. Each stream query has one or more input streams, from which it receives events, and one output stream, to which it transmits events.
In Apama, each event stream has a single generator but can have multiple consumers. Each stream or stream query is created within and owned by an Apama monitor instance. The streams and stream queries within a monitor instance are used to convert the events received by the monitor instance into added-value events. These added-value events are then available for use by standard EPL actions.
1 In Apama, the term 'stream' is used to refer both to the channel through which the events flow and also to the events flowing through the channel. Some members of the CEP fraternity use the term event channel to refer to the former and event stream to refer to the latter. In Apama, the term channel is already in use and so stream is used to refer to the 'event channels' connecting stream queries.