Dashboard data tables
To create dashboards, you should have an understanding of how Apama manages correlator data and makes it available for attachment to object properties.
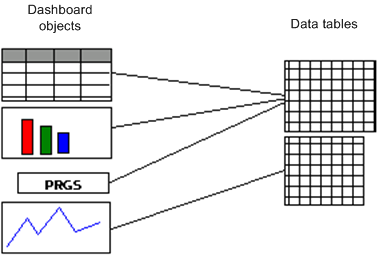
Apama makes scenario and DataView data available to dashboards as tabular data. Multiple data tables may be necessary for a dashboard. Any data table may have multiple objects in the dashboard attached to it. The relationship between dashboard objects and data tables is illustrated in the following diagram.
When a scenario variable or DataView field changes, the correlator generates an update event with details of the change. When this event is received by a dashboard, the dashboard updates one or more data tables and the changes are reflected in all attached objects.
Different data tables are used for each scenario or DataView. Data tables are not created until the first attachment requiring the data table is made. In the Dashboard Builder this happens when the attachment is defined. For a deployed dashboard, this happens when the dashboard is launched or loaded.
Once created, a data table exists for the life of the Builder process or deployed-dashboard session, although it may be purged of data if the corresponding scenario or DataView definition is deleted from the correlator or if the scenario instance or DataView item is deleted.
Apama filters the scenario instances or DataView items a user can see. Only those instances that the user is authorized for will be added to the user’s data tables. By default, these are the scenario instances or DataView items that the user created. See Administering Dashboard Security in Deploying Apama Applications for more information on dashboard authorization.
The following sections describe the different types of data tables: