EventService API
The Apama EventService API is layered on top of the EngineClient API which is described in
EngineClient API.
The EventService API allows client applications to focus on events and channels.
For a full reference of the EventService API in the different languages, refer to the following in your Apama installation directory:
For Java, refer to the Javadoc documentation at
doc\javadoc\index.html.
For .NET, refer to the .NET documentation at
doc\dotNet\index.html.
For examples of using the EventService API, see the following directories of your Apama installation:
 samples\engine_client\java\EventService
samples\engine_client\java\EventService samples\engine_client\dotnet\EventService
samples\engine_client\dotnet\EventServiceUsing the EventService API
An EventService instance can be created by calling the createEventService() method of the EventServiceFactory class. The factory class is the following:
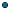
For Java, it is
com.apama.services.event.EventServiceFactory.
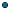
For .NET, it is
Apama.Services.Event.EventServiceFactory.
The host and port of the target engine is provided when creating the EventService instance.
Once the EventService instance has been created, it automatically takes care of connecting to the correlator in the background and of reconnecting when disconnected.
If the EventService is no longer needed, a cleanup should be performed by calling close() for Java or Dispose() for .NET, which will disconnect it and also ensure that any started background threads have been terminated.
Sending events
Clients wishing to use the EventService to send events into the correlator should use the send methods provided by it. The methods to send events generally have the term "send" in their names.
Receiving events
To use the EventService API, clients first need to create one or more EventServiceChannel objects to receive events from one or more channels. The methods to add/remove channels have the term "channel" in their names. Once an EventServiceChannel object is created, it can be used to receive events from the correlator. To receive events, clients need to add one or more event listeners on an EventServiceChannel object to receive either events of certain event types or all events from the channel.
The EventService API also provides an advanced mechanism to emulate request-response functionality. The EventServiceChannel object provides both synchronous and asynchronous mechanisms for request-response. With the synchronous mechanism, the client sends an event to the correlator and waits for the matching response event. With the asynchronous mechanism, the client sends an event to the correlator, and callback is invoked when a matching response event is received. The methods to emulate request-response functionality generally have "RequestResponse" in their names.