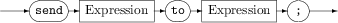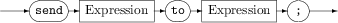The send . . . to statement
The send...to statement sends an event to the channel, context, sequence of contexts, or com.apama.Channel object that you specify.
Send...ToStatement
Rule components
The result type of the first Expression must be an event. It cannot be a string representation of an event.
The result type of the second Expression can be one of the following:
 string
string — The
send...to statement sends the event to the specified channel. All contexts and external receivers subscribed to that channel receive the event. If there are no subscribers to the specified channel or if no receivers are listening on the specified channel then the event is discarded.
 context
context — The
send...to statement sends the event to the back of the input queue of the specified context. The event expression is evaluated and the resulting event is sent to the input queue of only the specified context.
 sequence<context>
sequence<context> — The
send...to statement sends a copy of the event to the back of the input queue of each context in the specified sequence. The event expression is evaluated and the resulting event is sent to the input queue of each context in the sequence.
For example:
sequence <context> ctxs := [ c1, c2, c3 ];
Ping ping = Ping();
send ping to ctxs;
 com.apama.Channel
com.apama.Channel — The
send...to statement sends the event to the specified
Channel object. If the
Channel object contains a string, the event is sent to the channel with that name. If the
Channel object contains a context, the event is sent to that context. You cannot send an event to an empty context object.
You cannot send an event to a dictionary of contexts. However, it is a common pattern to send to a sequence generated by dictionary.values(). For example:
send x to d.values;
If the target context's input queue is full the sending context blocks and waits for space on the queue unless doing so would cause a deadlock. See
Deadlock avoidance when parallel processing.
Sent events are processed in the order they are sent. Sent events are put on the back of the input queue, behind any events already queued.
You must create the context before you send an event to the context. You cannot send an event to a context that you have declared but not created. For example, the following code causes the correlator to terminate the monitor instance:
monitor m {
context c;
action onload()
{
send A() to c;
}
}
If you send an event to a sequence of contexts and one of the contexts has not been created first then the correlator terminates the monitor instance. For details, see
Sending an event to a particular context.
Sending an event to a sequence of contexts is non-deterministic. For details, see
Sending an event to a sequence of contexts.
In a send...to statement, you cannot send an event that has a field of type action, chunk, listener, or stream.