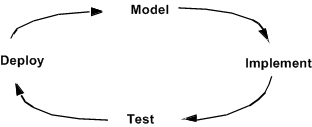
Steps for developing Apama applications
Typically, Apama development is an iterative cycle:
Multiple contributors with varying expertise can work concurrently to develop an Apama application.
The main steps for developing an Apama application include:
1. Model: Design your application. Important tasks are modeling the events that your application needs to handle and identifying the services that your application must provide.
2. Implement: Use Apama Studio to create an Apama project to contain your application files (EPL files, adapters, event files, scenarios, dashboards, and so on). Since Apama applications typically consist of many components, it is often possible to concurrently implement them, particularly if several people are working on the application:

Create scenarios in Apama Studio’s Event Modeler.

Write EPL or JMon programs in Apama Studio.

Develop Apama client applications.

Implement or develop adapters.

Create dashboards in Dashboard Builder.

Develop correlator plug-ins that extend the correlator’s standard features.
3. Test: Apama Studio provides a runtime perspective and Scenario Browser view that help test applications as they are built. You can also use Apama Studio’s Data Player in conjunction with the ADBC adapter to analyze application behavior before, or after, deployment. You can automate testing through the use of command-line clients.
4. Deploy: Use the Management and Monitoring console to start and manage Apama components, including correlators. Manage access to Apama applications with dashboards. Collect and manage event data with the ADBC (Apama Database Connector) standard Apama adapter and Apama Studio’s Data Player. Tune Apama applications for optimum performance.