Configuring an ADBC adapter
Apama Studio opens an adapter’s configuration file in the adapter editor. By default the file is displayed in the editor’s graphical view, which is accessed by clicking the Settings tab. The editor's other tabs are:
 Event Mapping
Event Mapping - Displays the Visual Event Mapper where you can quickly map Apama event fields to columns in a database table.
 XML Source
XML Source - Displays the configuration file’s raw XML code.
 Advanced
Advanced - Provides access to other configuration files associated with the adapter instance. These other files specify, for example, the instance's mapping rules, generated monitors and events responsibe for storing events in a database, and named queries.
To configure an instance of an ADBC adapter:
1. In the Project Explorer, expand the project’s Adapters node and open the adapter folder (either Adapter for ODBC, Adapter for JDBC, or Adapter for Sim).
2. Double-click the entry for the adapter instance you want to configure. The configuration file opens in the adapter editor. For example, a configuration file for an instance of the ADBC-JDBC adapter looks like this: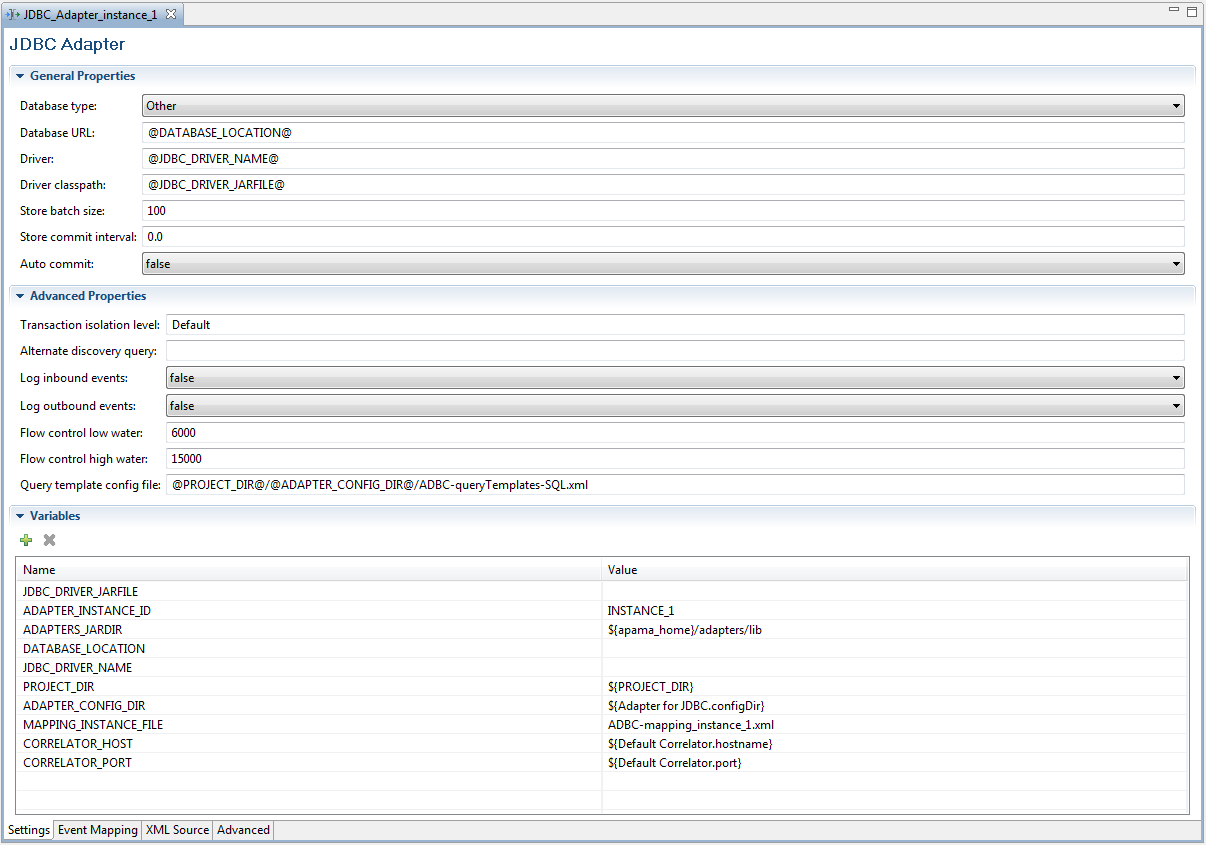
The Settings tab of the editor’s graphical display presents configuration information in three separate sections:
 General Properties
General Properties Advanced Properties
Advanced Properties Variables
VariablesFor an instance of the ADBC-ODBC adapter, the display is similar but with fewer items in the General Properties and Variables section. For an instance of the ADBC-Sim adapter, the display only shows the Variables section.
3. In the General Properties section, add or edit the following:
 Database Type
Database Type — This drop-down list allows you to select one of the database types from the list of certified vendors.
 Database URL
Database URL — This specifies the complete URL of the database. By default it uses the value of the
DATABASE_LOCATION variable; for more information on this variable see Step 5.
 Driver
Driver — For the ADBC-JDBC adapter, this specifies the class name of the vendor’s JDBC driver. By default it uses the value of the
JDBC_DRIVER variable as described in Step 5.
 Driver Classpath
Driver Classpath — For the ADBC-JDBC adapter, this specifies the classpath for the vendor’s driver jar file. By default it uses the value of the
JDBC_DRIVER_JARFILE variable as described in Step 5.
 AutoCommit
AutoCommit — This controls the use of the ODBC/JDBC driver autocommit flag. The default value is false.
 StoreBatchSize
StoreBatchSize — This defines the number of events (rows) to persist using the ODBC/JDBC batch insert API. The use of this setting will significantly increase store performance, but it is not supported by all drivers. A value of 100 is appropriate and will provide good performance in most cases.
If store performance is critical, testing is required to find the optimal value for the data and driver being used. The default is 0 which disables the use of batch inserts.
 StoreCommitInterval
StoreCommitInterval— This defines the interval in seconds before the ADBC adapter will automatically perform a commit for any uncommitted SQL command or store operations. The default value is 0.0 which disables the use of the timed commits.
4. In the Advanced Properties section, add or edit information for the following:
 Transaction Isolation Level
Transaction Isolation Level — This specifies what data is visible to statements within a transaction. The
Default level uses the default level defined by the database server vender. To change this setting, enter the appropriate value. For JDBC and ODBC the values can be
READ_UNCOMMITTED,
READ_COMMITTED,
REPEATABLE_READ, or
SERIALIZABLE.
 Alternate Discovery Query
Alternate Discovery Query — In most situations an entry here is not required and the ADBC
Discovery method lists the database available based on the
DATABASE_LOCATION variable. In some cases you may need to use a server vendor-specific SQL query statement to list the available databases, such as MySQL’s
SHOW DATABASES.
 Log Inbound Events
Log Inbound Events — A boolean that specifies whether or not the application logs inbound ADBC API events with information such as the exact query or command being executed. Logging these events is used for diagnostic purposes and eliminates the need to turn on IAF debug logging. The default is false; do not log incoming events.
 Log Outbound Events
Log Outbound Events — The same as
Log Inbound Events except for outbound ADBC API events.
 LogCommands
LogCommands — This property specifies whether or not the starts and completions of commands are written to the IAF log file. A value of "
true" (the default) logs this information; a value of "
false" turns logging off. This is useful in cases where logging the start and completion of a high rate of commands (many hundreds or thousands per second) does not add usable information to the log file.
 LogQueries
LogQueries — This property behaves identically to the
LogCommands property except that it specifies whether or not to log the start and completion of queries.
 FlowControlHighWater
FlowControlHighWater — This defines a maximum threshold for the number of query responses that have not been acknowledged by the ADBC flow control monitor. If this value is reached, the query will be paused until the number of outstanding acknowledgments decreases to the
FlowControLowWater value. This is used by the ADBC query flow control system to ensure the correlator does not get overwhelmed, especially when performing a fast as possible playback. The default value is 15000.
 FlowControlLowWater
FlowControlLowWater — This defines a threshold for the number of query responses not acknowledged by the ADBC flow control monitor before a query paused by
FlowControlHighWater is resumed. This is used by the ADBC query flow control system to ensure the correlator does not get overwhelmed, especially when performing a fast as possible playback. The default value is 6000.
 Query Template Config File
Query Template Config File — This specifies the file containing the query templates that are available to the application. By default, this uses a default template file created for the individual Apama Studio project.
You can add or edit values of the following additional advanced properties by clicking the XML tab and modifying the text of the configuration file:
 NumericSeparatorLocale
NumericSeparatorLocale — This allows the numeric separator used in the adapter to be changed, if necessary, to match the one used by the correlator. See
Configuring ADBC localization.
 FixedSizeInsertBuffers
FixedSizeInsertBuffers — This is an ODBC-specific property that allows you to change the default buffer size used when the
StoreData and
StoreEvent actions perform batch inserts. Apama uses the
FixedSizeInsertBuffers property along with the
StoreBatchSize property to determine how large the insert buffers should be. The value specified by
StoreBatchSize determines how many rows need to be buffered; the value specified by
FixedSizeInsertBuffers controls the size of the buffers for the columns. The default "true" uses a fixed buffer size of 10K bytes for each column. If the value is changed to "false", the size of the column buffers is determined dynamically by examining the database table into which the data will be inserted. Allowing the buffer size to be set dynamically can significantly reduce memory usage when performing batch inserts to database tables that contain hundreds of columns or when using a very large
StoreBatchSize.
5. In the Variables section, add or edit the appropriate values for the following tokens.
 ADAPTERS_JARDIR
ADAPTERS_JARDIR — For the ADBC-JDBC adapter this specifies the directory where the Apama adapter jar files are located. By default this is the Apama installation’s
adapters\lib directory.
 DATABASE_LOCATION
DATABASE_LOCATION —The location of the database for use with the ADBC Discovery API, for example,
jdbc:mysql://localhost/trades PROJECT_DIR
PROJECT_DIR — This specifies the location of the Apama project. By default this is automatically set by Apama Studio.
 ADAPTER_CONFIG_DIR
ADAPTER_CONFIG_DIR — This specifies the location of the adapter’s configuration files. By default this is automatically set by Apama Studio.
 CORRELATOR_PORT
CORRELATOR_PORT — This specifies the port used by the correlator. By default this is automatically set by Apama Studio.
 JDBC_DRIVER_NAME
JDBC_DRIVER_NAME — The class name of the driver, such as
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver JDBC_DRIVER_JARFILE
JDBC_DRIVER_JARFILE — The name of the data source driver file, for example,
C:/Program Files/MySQL/mysql-connector-java-5.1.7/mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar CORRELATOR_HOST
CORRELATOR_HOST — This specifies the name of the host machine where the project’s default correlator runs. By default this is automatically set by Apama Studio.
6. Specify the event mapping rules of the configuration that are specific to your application using the adapter editor's Visual Event Mapper, available on the Event Mapping tab. For more information on specifiying mapping rules, see The Visual Event Mapper. Copyright © 2013
Software AG, Darmstadt, Germany and/or Software AG USA Inc., Reston, VA, USA, and/or Terracotta Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA, and/or Software AG (Canada) Inc., Cambridge, Ontario, Canada, and/or, Software AG (UK) Ltd., Derby, United Kingdom, and/or Software A.G. (Israel) Ltd., Or-Yehuda, Israel and/or their licensors.
