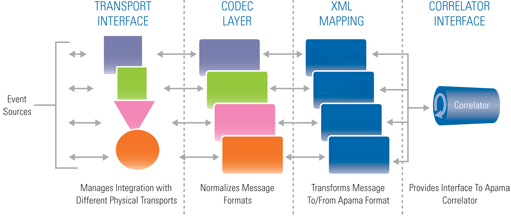
How Apama integrates with external data sources
You can connect Apama to any event data source, database, messaging infrastructure, or application. There are three ways to do this:

Implement Apama Integration Adapter Framework (IAF) adapters.

Develop client applications with Apama Java, .NET, and C++ APIs.

Create applications that use the correlator-integrated Java Message Service (JMS) connectivity.
Using IAF adapters to connect with external data sources
Apama’s Integration Adapter Framework (IAF) provides bi-directional connectivity with event sources and with your environment.
Apama adapters provide both connectivity and XML-based mapping between your application’s data format and Apama's internal format. The purpose of an adapter is to translate events from a proprietary format into Apama events. This lets the correlator analyze those events. Also, an adapter converts Apama events into your proprietary source format. This lets Apama send the events to an external service.
Adapters allow a single Apama application to efficiently monitor and analyze disparate event types within a common event processing scenario. For example, the same scenario can process events relating to foreign exchange (FX) aggregation, smart order routing and cross-asset trading in capital markets or cold chain automation in supply chain applications.
Within the IAF, Apama offers a range of standard adapters
for capital markets, infrastructure,
connectivity to data and messaging sources, and APIs for building custom adapters.
The IAF is a server component that adapters plug into for run-time invocation. You can develop an adapter with the IAF adapter library, along with whatever specific connection APIs you need to connect to your data service. Each adapter is structured so that the mapping of parameters between the source format and Apama format can be configured dynamically through XML.
The following figure shows the bi-directional operation of an adapter.
Examples of types of adapters include:

Middleware messaging adapters
Several middleware bus technologies are available on the market, including technologies by Tibco, IBM MQ Series, Vitria, WebMethods, SeeBeyond and others. When the middleware you are using is JMS-compliant, you can create applications that use the correlator-integrated JMS in place of an adapter.
Apama is able to interface with these technologies through an appropriate adapter. If the middleware bus offers publish and subscribe capabilities, then Apama can become a named endpoint like any other service. Apama is able to receive events from the bus and convert them, via an adapter, into Apama events for the correlator to process. An adapter can convert any events emitted by a correlator back into the native bus format.

Database adapters
Apama is able to connect to databases for a number of purposes, including querying historical state or storing key events as an audit trail in the corporate database. Most popular databases support a standard access protocol, such as ODBC or JDBC. The Apama Database Connector (ADBC) provides ODBC and JDBC adapters that use these standard access protocols to connect to your database.

Web Services adapter
The Apama Web Services Client adapter is usable across all Apama components. Interaction with the IAF is transparent to the application.

Custom real-time feed adapters
A number of companies provide real-time content as information feeds. Examples in the finance industry include Reuters, who provide a variety of stock and news feeds, and GLTrade, who provide bi-directional access to a variety of the world’s equities and derivatives exchanges. Many such companies use custom communications protocols to provide their data. However, Apama adapters have been easily developed for these and other bi-directional data services.
For complete information, see
The Integration Adapter Framework in
Developing Adapters.
Using Apama APIs to connect with external data sources
A range of APIs let you extend Apama at the dashboard, client, and correlator levels for integration with other environments, such as Java, .NET, C, or C++. In addition, you can extend correlator behavior with C and C++ plug-ins that can call external function libraries from within an application.
Using correlator-integrated JMS to connect with external data sources
Apama’s correlator-integrated JMS messaging provides an efficient way to receive and send JMS messages to and from Apama applications. It also provides for reliable messaging (guaranteed delivery) and duplicate detection.
Copyright © 2013
Software AG, Darmstadt, Germany and/or Software AG USA Inc., Reston, VA, USA, and/or Terracotta Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA, and/or Software AG (Canada) Inc., Cambridge, Ontario, Canada, and/or, Software AG (UK) Ltd., Derby, United Kingdom, and/or Software A.G. (Israel) Ltd., Or-Yehuda, Israel and/or their licensors.