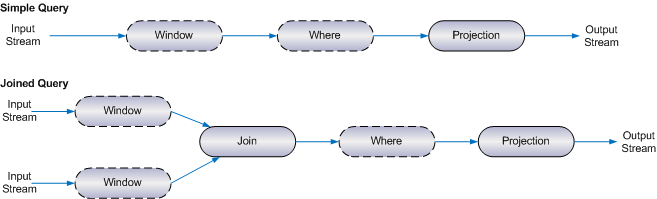
Each element of the stream query operates on the output of the previous part. To correctly define stream queries, it can be helpful to understand that items flow through the query and the correlator processes the parts of the query in the order shown in the following figure. In the figure, the dashed outlines indicate optional elements.
As items arrive on the input stream(s) and time elapses, the window definition for each stream identifies which items from that stream the query should be processing at any given moment. This includes partitioning, if it is specified. See
Adding window definitions to from and join clausesIn queries with two input streams, the correlator combines items from the two streams by means of a cross-join operation (a second
from clause) or an equi-join operation (a
join clause). See
Joining two streamsThe
where clause, if there is one, filters items. See
Filtering items before projection.
The projection definition defines how the query generates output items. This includes the
select clause, which has appeared in examples such as
Simple example of a stream network. See
Generating query results.