This document describes the utility "ADATST".
The following topics are covered:
The ADATST utility is used to fill the control block and the necessary buffers in order to issue Adabas commands.
Both the old ACB Adabas command interface and the new ACBX command interface are supported. For more information on the command interfaces please refer to the Command Reference documentation. Note that the ACB interface can be considered as a subset of the ACBX interface: Fields in the old ACB Adabas control block are also contained in the new ACBX control block (or the ABDs – the Adabas buffer descriptions) with the difference that some ACB fields are smaller then the corresponding fields in the new interface. In particular the buffer lengths have been increased that now Adabas buffers greater than 64 KB are possible. Switching between the interfaces is possible, but when you switch back to the old ACB interface you must be aware of the restrictions of the old ACB interface.
This utility is a multi-function utility. For more information about single- and multi-function utilities, see Adabas Basics -> Using Utilities -> Single- and Multi-function utility.
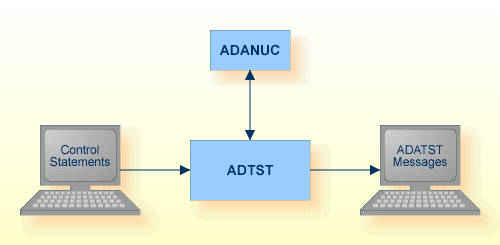
| Data Set | Environment Variable/ Logical Name |
Storage Medium |
Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control statements | stdin/ SYS$INPUT |
Utilities Manual | |
| ADATST messages | stdout/ SYS$OUTPUT |
Messages and Codes |
The utility writes no checkpoints.
Note
In the following, "string" is an
ASCII string or 0x followed by hexadecimal data.
The following control parameters are available:
A1 {=|:} string
A2 {=|:} string
A3 {=|:} string
A4 {=|:} string
A5 {=|:} string
A6 {=|:} string
ABD
ALOOP [= number]
CB
CBDUMP
CC = string
CID = string
CO1 = string
CO2 = string
CO3 = string
CO4 = string
CO5 = string
CO6 = string
CO7 = string
CO8 = string
M DBID = number
DLOOP
ELOOP
ERRORS = number
EXECUTE = { number | ISNQ }
FB [{=|:} string]
FB2 [{=|:} string]
FB3 [{=|:} string]
FBL = number
FB2L [= number]
FB3L [= number]
FILE = number
GO [= { number | ISNQ } ]
IB [= (number [,number]...)]
IBL = number
D INTERFACE = keyword
ISN = number
ISND = number
ISNI = number
ISNL = { number | ISN }
ISNQ = number
LOOP
MB = (number_buffers, number_isns)
D [NO]OUTPUT
OVERWRITE_RB = string
OVERWRITE_RB2 = string
OVERWRITE_RB3 = string
RB [{=|:} string]
RB2 [{=|:} string]
RB3 [{=|:} string]
RBL = number
RB2L [= number]
RB3L [= number]
READ_RB = string
READ_RB2 = string
READ_RB3 = string
RESPONSE = number
SB [{=|:} string]
SBL = number
SEC_PWD = string
SEC_UID = string
TIME
D [NO]TRACE
VB [{=|:} string]
VBL = number
D WAIT [= [time]]
WRITE_RB = string
WRITE_RB2 = string
WRITE_RB3 = string
A1 {=|:} string
This parameter sets the Additions 1 field.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
A2 {=|:} string
This parameter sets the Additions 2 field.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
A3 {=|:} string
This parameter sets the Additions 3 field.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
A4 {=|:} string
This parameter sets the Additions 4 field.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
A5 {=|:} string
This parameter sets the Additions 5 field.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
A6 {=|:} string
This parameter sets the Additions 6 field.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
ABD
This parameter is available only after specifying INTERFACE=ACBX. It displays the Adabas buffer definitions for the Adabas buffers that are currently defined.
ALOOP [= number]
This parameter opens a loop to add more lines. `number' is a line number. If a line number is specified, new lines are added from that point, overwriting existing lines; if no number is specified, new lines are added at the end. Close the loop with ELOOP.
CB
This function displays the contents of the control block.
If the parameter INTERFACE=ACB is specified, only the fields contained in the old ACB Adabas control block are displayed.
If the parameter INTERFACE=ACBX is specified, the fields contained in the new ACBX Adabas control block but not in the old ACB Adabas control block are also displayed.
CBDUMP
This function dumps the control block in hex.
CC = string
This parameter specifies the command code.
CID= string
This parameter specifies the command ID.
After issuing the command ET, BT,
or CL, CID is set to binary zero. If
the command ET or BT is issued
with command option 1 set to ‘S’, CID is not reset
to binary zero.
CO1 = string
This parameter sets the command option 1.
CO2 = string
This parameter sets the command option 2.
CO3 = string
This parameter sets the command option 3.
CO4 = string
This parameter sets the command option 4.
CO5 = string
This parameter sets the command option 5.
CO6 = string
This parameter sets the command option 6.
CO7 = string
This parameter sets the command option 7.
CO8 = string
This parameter sets the command option 8.
DBID = number
This parameter specifies the database to be used.
DLOOP
This function displays a saved command loop.
ELOOP
This function terminates a loop.
ERRORS = number
This parameter specifies the number of errors permitted before termination occurs.
EXECUTE = { number | ISNQ }
This parameter executes a loop `n' times, where `n' is specified by `number' or by ISNQ. Enter CTRL/C to terminate a loop.
FB [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the first format buffer or enter data into the format buffer. The length is set implicitly.
FB2 [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the second format buffer or enter data into the format buffer. The length is set implicitly.
FB3 [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the third format buffer or enter data into the format buffer. The length is set implicitly.
FBL = number
This parameter defines the first format buffer length in the control block.
FB2L = number
This parameter defines the second format buffer length in the control block.
FBL3 = number
This parameter defines the third format buffer length in the control block.
FILE = number
This parameter specifies the file number.
GO [= { number | ISNQ } ]
This function calls Adabas once or `n' times, where `n' is specified by `number' or ISNQ. Enter CTRL/C to terminate a loop.
IB [= (number [,number]...)]
This parameter is used to display the ISN buffer or enter ISNs. The length is set implicitly.
IBL = number
This parameter specifies the ISN buffer length in the control block.
INTERFACE = keyword
This parameter is used to switch between the old and new Adabas command interface. Valid keywords are ACB and ACBX. The default is ACB. After INTERFACE = ACB has been specified, Adabas calls are performed with the old ACB Adabas interface - any fields that are only contained in the new ACBX Adabas control block and additional format buffers and record buffers are ignored. You can switch between the old and the new Adabas interface in one Adabas session.
ISN = number
This parameter sets ISN with the number supplied.
ISND = number
This parameter subtracts `number' from ISN.
ISNI = number
This parameter adds `number' to ISN.
ISNL = { number | ISN }
This parameter is used to set the ISN lower limit with the number supplied, or to move the ISN from the control block into the ISN lower limit.
ISNQ = number
This parameter specifies the ISN quantity with the number supplied.
LOOP
This function defines the start of a loop. All commands that follow will be saved until an ELOOP is entered.
MB = (number_buffers, number_isns)
This parameter defines the number of multifetch buffers and the number of IS entries that can be stored in a multifetch buffer. number_buffers may be a number between 0 and 3. number_isns must be a number >0.
The MB parameter can only be specified after INTERFACE = ACBX has been specified.. Since multifetch buffers are pure output buffers, it is not possible to enter content into the multifetch buffers.
Once multifetch buffers have been specified, you can display their contents with the RB, RB 2 and RB3 parameters.
[NO]OUTPUT
If this option is set to NOOUTPUT, no messages are output when calling Adabas `n' times. Only error messages will be printed.
The default is OUTPUT.
OVERWRITE_RB = string
This parameter specifies the name of an existing file to which the contents of the first record buffer are written. The current contents of the file will be overwritten.
OVERWRITE_RB2 = string
This parameter specifies the name of an existing file to which the contents of the second record buffer are written. The current contents of the file will be overwritten.
OVERWRITE_RB3 = string
This parameter specifies the name of an existing file to which the contents of the third record buffer are written. The current contents of the file will be overwritten.
RB [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the first record buffer or enter data into the first record buffer. For input to a file, the length is set implicitly.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
If you display the first record buffer, and at least one multifetch buffer has been defined with the MB parameter, the first multifetch buffer is also displayed.
RB2 [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the second record buffer or enter data into the second record buffer. For input to a file, the length is set implicitly.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
If you display the second record buffer, and at least two multifetch buffers have been defined with the MB parameter, the second multifetch buffer is also displayed.
RB3 [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the third record buffer or enter data into the third record buffer. For input to a file, the length is set implicitly.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
If you display the third record buffer, and at three multifetch buffer have been defined with the MB parameter, the third multifetch buffer is also displayed.
RBL = number
This parameter specifies the first record buffer length in the control block.
RB2L = number
This parameter specifies the second record buffer length in the control block.
RB3L = number
This parameter specifies the third record buffer length in the control block.
READ_RB = string
This parameter specifies the name of a file that is read into the first record buffer.
READ_RB2 = string
This parameter specifies the name of a file that is read into the second record buffer.
READ_RB3 = string
This parameter specifies the name of a file that is read into the third record buffer.
RESPONSE = number
This parameter displays the error text for the given nucleus response code.
SB [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the search buffer or enter data into the search buffer. The length is set implicitly.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
SBL = number
This parameter specifies the search buffer length in the control block.
SEC_PWD = string
This parameter sets the password for the credential that is used for authentication..
The credentials are checked by the Adabas server during command processing.
When used, the control parameter SEC_UID must also be set, if either value is missing or invalid an Adabas error is returned.
SEC_UID = string
This parameter sets the user ID credential that is used for authentication.
The credentials are checked by the Adabas server during command processing.
When used, the control parameter SEC_PWD must also be set, if either value is missing or invalid an Adabas error is returned.
TIME
This function marks the current time, and displays the difference between this and the last time mark.
[NO]TRACE
This option traces execute loops.
The default is NOTRACE.
VB [{=|:} string]
This parameter is used to display the value buffer or enter data into the value buffer. The length is set implicitly. If `string' equals RB, the record buffer is moved into the value buffer.
If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
VBL = number
This parameter specifies the value buffer length in the control block.
WAIT [= seconds]
This parameter causes ADATST to wait for a given period. The waiting time is entered in seconds. Once the time is set, you can wait for the same period by entering 'WAIT' without any additions.
The default time is 10 seconds.
adatst: wait = 15
ADATST waits for fifteen seconds.
WRITE_RB = string
This parameter specifies the name of a file to which the contents of the first record buffer are written. The record buffer is only written if a file with the specified name does not already exist.
WRITE_RB2 = string
This parameter specifies the name of a file to which the contents of the second record buffer are written. The record buffer is only written if a file with the specified name does not already exist.
WRITE_RB3 = string
This parameter specifies the name of a file to which the contents of the third record buffer are written. The record buffer is only written if a file with the specified name does not already exist.