The current version of Adabas includes the following extensions, which enable you to work more easily with Adabas Analytics:
| Extention | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ADAELP | Event log report. Used to print events from the Adabas Anlytics event log. |
| EALCONFIG | Event Analytics configuration tool. Used to help you set up the Adabas Analytics component. |
This section describes the utility "ADAELP".
The following topics are covered:
The ADAELP utility prints events from an event log created by Adabas Analytics.
Note:
Event logging must be enabled and the replication user exit must be
loaded in order to write event logs. For further information see the section
Concepts.
The ADAELP parameters USER_ID, HOSTNAME and EVENT_TIMESTAMP select a subset of the events in the event log.
In the interactive mode, ADAELP displays the selected events when the keyword LIST is entered. If ADAELP is called with parameters, the selected events are displayed immediately.
Events are displayed as follows: a first line with the event type is followed by lines that contain the field data of the event in question. The display of an event is concluded with the event type being repeated on the last line.
start read event event_timestamp=16-JUL-2015 11:51:01.977020 dbid=163 file_number=1 command_code=L5 response_code=0 isn=993 pid=6772 hostname=PCST01 user_id=st tsid=68 ba 56 02 fb 1a 05 00 end read event
This utility is a single-function utility.
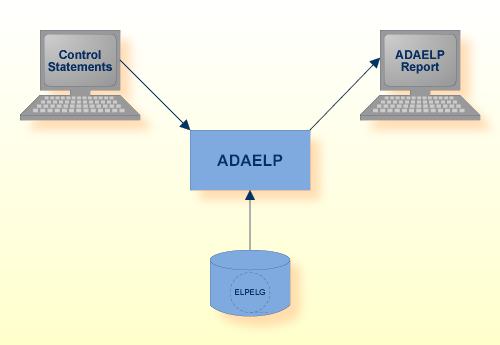
| Data Set | Environment Variable/ Logical Name |
Storage Medium |
Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Event log | ELPELG | Disk | |
| Control statements | stdin | see section Control Parameters | |
| ADAELP report | stdout |
The utility writes no checkpoints.
The following control parameters are available:
D DBID = number EVENT_TIMESTAMP = ([absolute-date][,[absolute-date]]) HOSTNAME = string LIST USER_ID = string
DBID = number
This parameter specifies the database ID of the database for which the event log was written.
EVENT_TIMESTAMP = ([absolute-date][,[absolute-date]])
This parameter selects the log records in the range specified by the optional date strings. The date strings must correspond to the following absolute date and time format:
dd-mmm-yyyy[:hh:mm:ss[.mmmmmm]]
Leading zeroes in the date and time specification may be omitted. Any numbers not specified are set to 0, for example 28-jul-2015 is equivalent to 28-jul-2015:00:00:00.000000.
By default, all log records are selected.
adaelp: event_timestamp = 8-aug-2015
The event with event_timestamp 8-AUG-2015 00:00:00 is selected.
adaelp: event_timestamp = (8-aug-2015:12,)
All events with time_stamp from 8-AUG-2015 12:00:00 onwards are selected.
adaelp: event_timestamp = (,8-aug-2012:12:34)
All events with time_stamp before 8-AUG-2015 12:34:00 are selected.
adaelp: event_timestamp = (16-JUL-2015 11:51:01.977020, 16-JUL-2015 11:51:02.177000)
All events with event_timestamp from 16-JUL-2015 11:51:01.977020 to 16-JUL-2015 11:51:02.177000 are selected.
HOSTNAME = string
This parameter selects all events with the hostname specified by 'string'. The length of the parameter value is limited to 8 characters.
LIST
This parameter lists the events selected with the parameters DBID, EVENT_TIMESTAMP, HOSTNAME and USER_ID.
USER_ID = string
This parameter selects all events with the user ID specified by 'string'. The length of the parameter value is limited to 8 characters.
If multiple selection criteria are specified, they are combined by a logical AND, e.g.
event_timestamp=(8-aug-2015:12:34,), user_id = guest, hostname = machine3
This selects all events after 8-aug-2015:12:34 with user_id = guest and hostname = machine3.
A simple configuration tool (EALCONFIG) is provided to help you set up the Adabas Analytics component. All configuration parameters are stored in the appropriate DBnnn.INI file in the database directory. The database with a valid DBnnn.INI file must exist.
Compared to the version provided with the Adabas Version 6.5.0 package, the new version of EALCONFIG has the following major differences:
New subtopics TARGET_EAL_SERVER and TARGET_NUCELG;
The items SWITCH_AFTER_EVENTS and SWITCH_AFTER_TIME are moved to TARGET_NUCELG;
The item TARGET_NUCELG is ignored if TARGET_EAL_SERVER exists;
The new event types NAT_INSERT, NAT_READ, NAT_UPDATE, NAT_DELETE, NAT_COMMIT, NAT_ROLLBACK, ADA_PERF and ADA_NAT_PERF are supported.
Notes:
adaini
dbid=<nnn> delete topic=event_analytics topic=TARGET_EAL_SERVER
item=*.
adaini dbid=<nnn> show topic=event_analytics.
The configuration tool will ask you for each parameter one at a time. It does not accept command line parameters.
The following parameters are requested by the configuration tool. The current settings or default values are shown in brackets ([]). Pressing the Enter key without any input will keep the current setting.
- Dbid
The database ID of the database to be configured for Adabas Analytics.
- Activate
Enable or disable the event logging. Possible values are yes and no, the default is yes.
- Destination of Events
Choose SERVER if you want to send the events to the Adabas Analytics server. Choose FILE if you want to send the events to a file. The default is SERVER.
- File name (only if destination FILE is selected)
The fully-qualified path name for the log file. The default is $ADADATADIR/dbnnn/NUCELG or %ADADATADIR%\dbnnn\NUCELG.
- Filter events for files
A list of database file numbers for which the event logging is to be performed. For multiple values, specify the list surrounded by brackets, e.g. '(10,11,12,30-40,100)'; for all files enter an asterisk '*'. The default value is '*'.
- Filter for events
A list of event types which will be logged. The default is all events. For multiple values, specify the list surrounded by brackets, e.g. '(INSERT,UPDATE,COMMIT)', for all events enter an asterisk '*'. For further information about the supported event types, see Adabas Analytics Event Types.
- Switch log file after events (only if destination FILE is selected)
The number of events that occur before starting a new log file. The default is never to switch.
- Switch log file after time (only if destination FILE is selected)
The number of seconds that elapse before starting a new log file. The default is never to switch.
- Host name (only if destination SERVER is selected)
This is the host name where the analytics server is running. The default is localhost.
- Port number (only if destination SERVER is selected)
This is the port number that the analytics server listens to. The default is 6521.
- Reconnect timeout (only if destination SERVER is selected)
If the connection between the Adabas nucleus and the analytics server is lost, this parameter specifies the time in seconds that the Adabas nucleus waits until it tries to reconnect to the analytics server. The default is 1.
- Maximum number of reconnect attempts (only if destination SERVER is selected)
If the connection between the Adabas nucleus and the analytics server is lost, this parameter specifies the number of reconnect attempts. The default is 0, which means 'try forever'.
Note:
If the maximum number of attempts is not 0, and if the maximum number of reconnect attempts is reached without reconnecting successfully, event logging will be deactivated.- Nucleus behaviour in case of error (only if destination SERVER is selected)
Select ABORT if you want to abort the Adabas nucleus if a connection error occurs between the Adabas nucleus and the analytics server. Select IGNORE if you want to continue with the Adabas nucleus if a connection error occurs between the Adabas nucleus and the analytics server.
The following example shows a first run of the configuration tool. The result of this configuration will be: for the files 10,11,12,30 to 40 and 100, the events for insert, update and commit commands are logged in the file /opt/softwareag/Adabas/db199/NUCELG.0001. After 86400 seconds (i. e. 24h) or after 1000000 events (depending on which occurs first), the current NUCELG file will be closed and a new file with an increased suffix will be created (NUCELG.0002, NUCELG.0003, ...).
$> ealconfig
Adabas Analytics Configuration Tool
Current/default values are shown in '[]', press <enter> to keep these values.
Multiple values have to be enclosed in brackets.
Please enter the dbid: 199
Do you want to activate event logging [YES|NO]? [YES] yes
Please enter the file name for the EAL log [/opt/softwareag/Adabas/db199/NUCELG]:
Filter events for files. Only for the specified files the events are logged.
Format: (5,8,10,20-30,40-50), (*) for all files.
Please enter the file list [*]: (10,11,12,30-40,100)
Filter events. Only the specified events are logged.
Available event types:
(INSERT, READ, UPDATE, DELETE, COMMIT, ROLLBACK,
NAT_INSERT, NAT_READ, NAT_UPDATE, NAT_DELETE, NAT_COMMIT, NAT_ROLLBACK,
ADA_PERF, ADA_NAT_PERF), (*) for all events.
Please enter the event type list [*]: (INSERT,UPDATE,COMMIT)
Log file switching. You can begin a new log file after a number of events occurred and/or after a certain time.
Please enter the number of events ('0' - do not switch) []: 1000000
Please enter the number of seconds ('0' - do not switch) []: 86400
Saving changes to DB199.INI file.
Terminated.
The resulting DB199.INI file then contains the following entry:
[EVENT_ANALYTICS]
ACTION = YES
[TARGET_NUCELG]
SWITCH_AFTER_EVENTS = 1000000
SWITCH_AFTER_TIME = 86400
[TARGET_NUCELG-END]
[FILTER]
FILES = (10,11,12,30-40,100)
EVENT_TYPES = (INSERT,UPDATE,COMMIT)
[FILTER-END]
[EVENT_ANALYTICS-END]
The following example shows a first run of the configuration tool. The result of this configuration will be: for the files (9,11,202-205), the ADA_NAT_PERF event is logged and sent to the analytics server. The analytics server is running on localhost, the port number is 6521. If the connection between the Adabas nucleus and the analytics server is lost, the Adabas nucleus ignores the disconnect, but still tries to reconnect to the analytics server every second.
$> ealconfig
Adabas Analytics Configuration Tool (v6.5.1)
Current/default values are shown in '[]', press <enter> to keep these values.
Multiple values have to be enclosed in brackets.
Please enter the dbid: 199
Do you want to activate event logging [YES|NO]? [YES]
Destination of Events: You can send events to the Adabas Analytics Server,
the default, or write the events into a file.
Which destination do you want [SERVER|FILE]? [SERVER]
Filter events for files. Only for the specified files the events are logged.
Format: (5,8,10,20-30,40-50), (*) for all files.
Please enter the file list [(9,11,202-205)]:
Filter events. Only the specified events are logged.
Available event types are:
(INSERT, READ, UPDATE, DELETE, COMMIT, ROLLBACK, NAT_INSERT, NAT_READ,
NAT_UPDATE, NAT_DELETE, NAT_COMMIT, NAT_ROLLBACK, ADA_PERF, ADA_NAT_PERF),
(*) for all events.
Please enter the event type list [*]: ADA_NAT_PERF
Please enter the host name where the analytics server is running [localhost]:
Please enter the port number of the analytics server [6521]:
Please enter the reconnect timeout (seconds) [1]:
Please enter the maximum number of reconnect attempts ('0' - try forever) [0]:
The behaviour of the nucleus for errors with the analytics server.
The nucleus can ABORT or just ignore the error and try to reconnect to the
Analytics Server.
Please enter one of the available actions: ABORT, IGNORE [IGNORE]:
Saving changes to DB199.INI file.
Terminated.
The resulting DB199.INI file then contains the following entry:
[EVENT_ANALYTICS]
ACTION = YES
[FILTER]
EVENT_TYPES = ADA_NAT_PERF
FILES = (9,11,202-205)
[FILTER-END]
[TARGET_EAL_SERVER]
HOST = localhost
MAX_RETRIES = 0
ON_ERROR = IGNORE
PORT = 6521
RECONNECT_TIMEOUT = 1
[TARGET_EAL_SERVER-END]
[EVENT_ANALYTICS-END]
Adabas Analytics uses a new topic ([EVENT_ANALYTICS]) in the configuration file DBnnn.INI. An example of how this topic might look is shown in the examples above.
This section describes the keywords and subtopics contained in the [EVENT_ANALYTICS] topic.
Note:
All of the keywords and subtopics are
optional.
This keyword activates/deactivates Adabas Analytics. If this keyword is omitted, Adabas Analytics is switched off. Valid keywords are YES and NO.
This keyword is used to switch to a new NUCELG file after <count> events have been written to the NUCELG file. If this keyword is omitted, all events are logged to a single NUCELG file.
This keyword is used to switch to a new NUCELG file after <time in seconds> has passed and a new event is to be generated. If this keyword is omitted, all events are logged to a single NUCELG file.
The subtopic FILTER has 2 keywords: FILES and EVENT_TYPES. These keywords are used to determine which types of events are generated for which Adabas files.
This keyword specifies the Adabas files that are to be active for eventing. You can specify a list of files; the list can contain single files (<file1>, <file2>) or a range of files (<file3> - <file4>). If this keyword is omitted, events are generated for all Adabas files in the database.
This keyword specifies the types of events that are generated. The details of each event type are described in the section Adabas Analytics Event Types. If this keyword is omitted, all event types are generated for the files specified by the FILES keyword.
The filter mechanism gives you control over the events that are generated.
You can filter the events by the following criteria:
Adabas file number;
Event type.
You can filter by Adabas file number only, by event type only or you can combine both filters. For further information about the syntax and semantics of the filters for FILES and EVENT_TYPES, see the section Parameters of Adabas Analytics in the Configuration File DBnnn.INI.
The file DBnnn.INI contains the topic EVENT_ANALYTICS and the subtopic FILTER.
[EVENT_ANALYTICS]
ACTION = YES
[TARGET_NUCELG]
SWITCH_AFTER_EVENTS = 1000000
SWITCH_AFTER_TIME = 86400
[TARGET_NUCELG-END]
[FILTER]
FILES = (10,11,12,30-40,100)
EVENT_TYPES = (INSERT,UPDATE,COMMIT)
[FILTER-END]
[EVENT_ANALYTICS-END]
This entry results in events being generated for the Adabas files 10,11,12,30-40 and 100. The events are limited to the types insert, update and commit. After 86400 seconds (24 hours) or after 1000000 events (depending on which comes first), the current NUCELG file will be closed, and a new file with an increased suffix will be created (NUCELG.0002, NUCELG.0003 ...).
Adabas Analytics currently supports 7 types of conceptual distinct events in two categories. Six events belong to the category auditing, and one event belongs to the category performance monitoring. For each of the 7 conceptual events, there are two manifestations: events with/without Natural-specific information, thus resulting in an overall of 14 distinct event types. Events containing Natural information are prefixed with “NAT_”, events without Natural information do not have a prefix.
- INSERT
A new record has been created, triggered by Adabas commands of the type Nx.
- NAT_INSERT
Same as INSERT, but with additional Natural information.
- READ
A record has been searched, triggered by Adabas commands of the types Lx and Sx.
In the case of Read commands (Lx) with the multifetch option specified, a read event will be generated for each record that can be read. If a record cannot be read because it is held exclusively by another user, a read event with response code 145 will be triggered for this record, but only if the return option (O) was specified.
- NAT_READ
Same as READ, but with additional Natural information.
- UPDATE
A record has been modified, triggered by an Adabas command of the type A1.
- NAT_UPDATE
Same as UPDATE, but with additional Natural information.
- DELETE
A record has been removed, triggered by an Adabas command of the type E1.
- NAT_DELETE
Same as DELETE, but with additional Natural information.
- COMMIT
A transaction has been committed, triggered by Adabas commands of the types ET and CL.
- NAT_COMMIT
Same as COMMIT, but with additional Natural information.
- ROLLBACK
A transaction has been backed out, triggered by an Adabas command of the type BT, and also by any other command that results in the nucleus response code 9.
- NAT_ROLLBACK
Same as ROLLBACK, but with additional Natural information.
- ADA_PERF
A command was processed by Adabas. This event contains additional information regarding the command, such as time taken and command options.
- NAT_ADA_PERF
Same as ADA_PERF, but with additional Natural information.
The fields in the event types (which can be displayed using the utility ADAELP) contain the following information:
| Field | Information Contained |
|---|---|
| event_timestamp | Creation time of this event. |
| dbid | Adabas database ID. |
| file_number | Adabas file number. |
| command_code | Adabas command code. |
| response_code | Adabas response code. |
| isn | Adabas ISN. |
| pid | Process ID of the Adabas client. |
| hostname | Machine name of the Adabas client. |
| user_id | User ID of the Adabas client. |
| tsid | Unique marker of the Adabas client. |
| natapplication* | Name of the Natural application issuing the call. |
| natprogram* | Name of the Natural program issuing the call. |
| natcount* | Number of ADABAS calls since the last IO. |
| natexec* | Number of times a Natural object has been executed (internal). |
| natlevel* | Natural call level of the program executed. |
| natuser* | The Natural user issuing the call. |
| natstatement* | Natural statement number. |
| natlib* | The Natural library issuing the call. |
| natrpcclientuid* | Natural RPC client user ID. |
| natrpcid* | Natural RPC ID. |
| natrpcconvid* | Natural RPC conversation ID. |
| natsecgroup* | Natural security group. |
| additions1 | Contains the additions1field of the issued call. |
| command_duration | Contains the time taken, in microseconds, that Adabas took to process the call |
| copt1 | Contains the value of command option 1 of the processed call |
| copt2 | Contains the value of command option 2 of the processed call |
*) These fields are only available when using events with Natural information.