A column physical element is used to add Adabas-specific attributes to a column.
This element is part of the column element. This clause is only allowed in CREATE TABLE/ CREATE TABLE DESCRIPTION or a CREATE CLUSTER/CREATE CLUSTER DESCRIPTION statements.
Syntax:
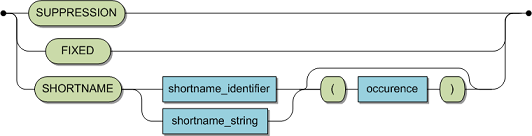
|
shortname_identifier |
Specifies an Adabas short name for a column. |
|
string literal |
Represents the Adabas short name for a column. |
|
numeric literal |
Optional. Only applies to MUs and PEs. Specifies a rotated field. Value must be less or equal to 191. |
The following table associates an Adabas SQL Gateway Embedded SQL option with the corresponding Adabas option:
|
Adabas SQL Gateway Embedded SQL |
Adabas |
|---|---|
|
FIXED |
FI |
|
SUPPRESSION |
NU |
The SHORTNAME identifier specifies the Adabas short name of the corresponding Adabas field.
If the shortname_identifier is a numeric literal, it specifies a rotated field. Each occurrence is mapped to an individual column:
If a particular MU or PE field (semantically) has a non varying number of occurrences, then the field can be 'rotated.' Each occurrence is mapped to an individual column. For example, if an MU has 12 occurrences and each represents a month, then each occurrence could be mapped to the columns January through to December. A similar technique can be used for PEs, although each field within each occurrence must be individually mapped to a column.
An Adabas short name must consist of exactly two characters; the first character must be between A and Z and the second can be between A and Z or between 0 and 9. Do not use the short names E0 to E9; they are Adabas reserved names. If your short name is a reserved word you must represent it in string format. For example, reserved word AS would be represented by SHORTNAME 'AS'.
The short name specification is not case sensitive.
Do not combine the FIXED keyword with the SUPPRESSION attribute.
Use the FIXED and SUPPRESSION keywords only in the CREATE TABLE DESCRIPTION and CREATE CLUSTER DESCRIPTION statements. The underlying Adabas field must have these attributes.
Do not use the PRIMARY KEY constraint with the SUPPRESSION attribute, .
Do not use the NOT NULL attribute with either the SUPPRESSION attribute with the UNIQUE constraint or the SUPPRESSION attribute with the HAVING UNIQUE INDEX clause.
The column physical element is not part of the Standard.
None.
Example:
The following example stores bonus and sales for each month in a multiple-value field (each month is one occurrence). Each column is then rotated to be seen in one table (each month is a column of this table). An example of such a table description with rotated columns is:
CREATE TABLE DESCRIPTION rotated_table
DATABASE NUMBER 151 FILE NUMBER 53
(
id CHAR(20) SHORTNAME "AA",
january_bonus INTEGER SHORTNAME "DA"(1),
january_sales INTEGER SHORTNAME "DB"(1),
february_bonus INTEGER SHORTNAME "DA"(2),
february_sales INTEGER SHORTNAME "DB"(2)
...
december_bonus INTEGER SHORTNAME
"DA"(12),
december_sales INTEGER SHORTNAME "DB"(12),
)
where: DA and DB are the short names for the fields within the periodic group.