A set is skewed if one of its tails is longer than the other. A set has a positive skew if it has a long tail in the positive
direction. A set has a negative skew if it has a long tail in the negative direction. A set is perfectly symmetrical if it
has no skew. Though negatively skewed sets do occur, sets with positive skews are more common than sets with negative skews.
Skew can be calculated as:
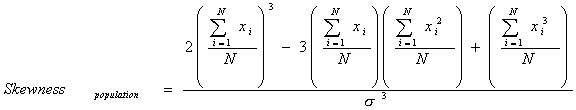
As a general rule, the mean is larger than the median in positively skewed sets and less than the median in negatively skewed
sets. The standard deviation is not a good measure of spread in highly skewed distributions and should be augmented in those
cases by the semi-interquartile range. Skew is sometimes called the third moment of a set. A set with a skew of zero is one
that is not lopsided in either direction. A set with a skewness of 1 or more is highly skewed. A set with a skewness between
0 and 1/2 is considered moderately skewed. If the skewness is less than 1/2 then the distribution is fairly symmetrical.
numeric_exp should be a numeric column or a numeric expression.