COBOL host variables used in SQL statements must be declared within the SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION and END DECLARE SECTION statements as well as in the COBOL DATA DIVISION. There may be any number of SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTIONs. The host variable definition must be a valid COBOL data declaration, as described below. Adabas SQL Gateway Embedded SQL allows the use of single host variables and host variable structures.
COBOL host structures are a named set of COBOL single host variables and must conform to the ANSI Standard for COBOL.
The use of COBOL host structures within SQL statements is an Adabas SQL Gateway Embedded SQL extension and not part of the SQL ANSI Standard.
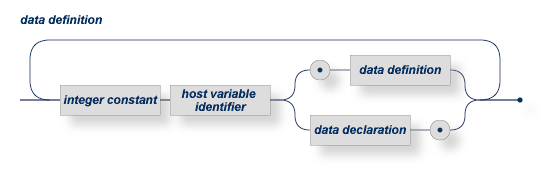
|
integer constant |
level number as described in the ANSI standard for COBOL |
|
host variable identifier |
specifies the identifier of the COBOL single variable or structure. Any valid COBOL identifier may be used. |
|
data definition |
recursive definition for nested structure level specification. |
|
data declaration |
see the syntax diagram below. |
Example of a structure definition:
01 LEVEL1.
02 LEVEL2.
05 ELEMENT1 PIC 9.
05 ELEMENT2 PIC 9.
Within embedded SQL statements the COBOL naming qualification rules for structure elements do not apply. Instead they must be specified top down to read "LEVEL1. LEVEL2.ELEMENT1" as shown in the example above.
In COBOL statements, however, the structure elements must still be specified (bottom up) according to the ANSI COBOL rules: e.g. "ELEMENT1 IN LEVEL2 IN LEVEL1".
When referencing a structure element which is not uniquely identified within the compilation unit it must be sufficiently qualified with enough containing structure identifiers to unambiguously identify the variable concerned. If for example the identifier ELEMENT1 has been used in more than one structure definition then it must be qualified to give either LEVEL2.ELEMENT1 or even if necessary LEVEL1.LEVEL2.ELEMENT1.
For more information about the general usage of host variables within SQL, see the topics under Common Elements in this help file.
The declaration must conform to the following COBOL syntax.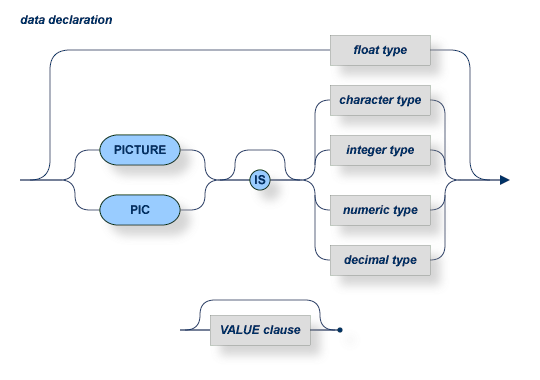
VALUE clause specifies any valid COBOL VALUE clause.
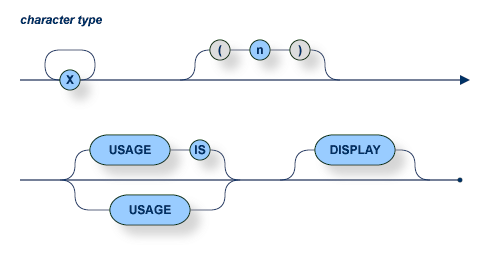
The number of significant characters must not exceed 253.
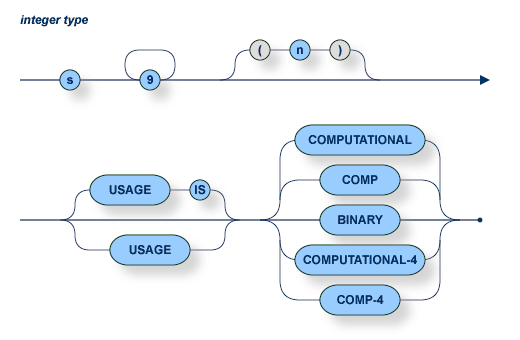
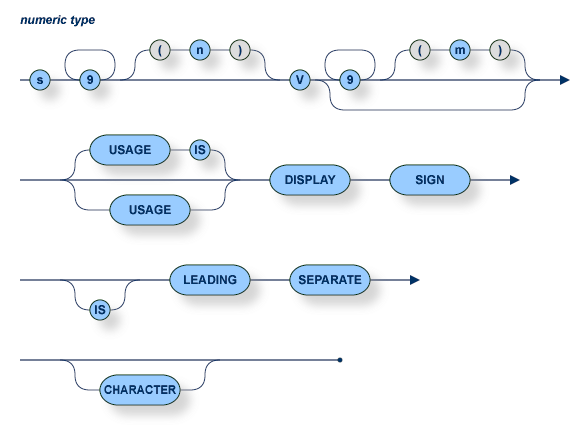
The number of digits must not exceed 9.
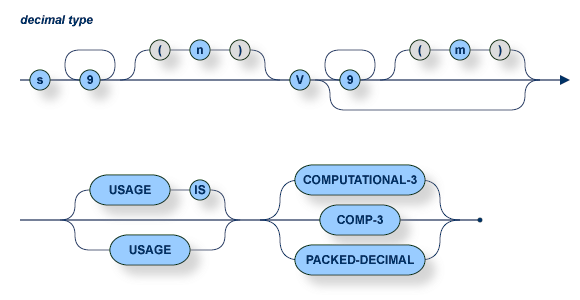
The number of digits must not exceed 27.
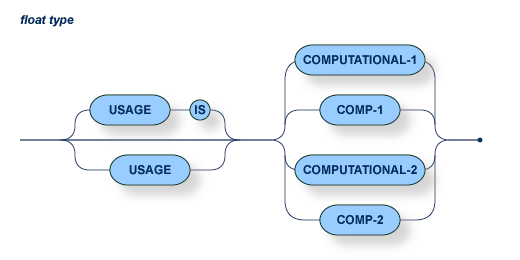
The number of digits must not exceed 27.
The following table shows the conversion of COBOL data types to SQL data types and vice versa:
|
COBOL Data Types |
SQL Data Types |
|
character |
CHARACTER |
|
char (array) |
BINARY |
|
integer (5-9 digits) |
INTEGER |
|
integer (1-4 digits) |
SMALLINT |
|
numeric |
NUMERIC |
|
decimal |
DECIMAL |
|
float (comp-1) |
REAL |
|
float (comp-2) |
DOUBLE-PRECISION |
For more details on SQL data types and their usage in SQL statements refer to Common Elements in the Adabas SQL Gateway Embedded SQL Reference. The number of digits for an integer type must not exceed 9.