Adabas Fastpath can be used to optimize Adabas databases that are remote to the client process while automatically maintaining the integrity of data in the Adabas Fastpath buffer.
The following graphic shows the communication components and path involved in a client query, without Adabas Fastpath, when the data resides in a remote Adabas server:
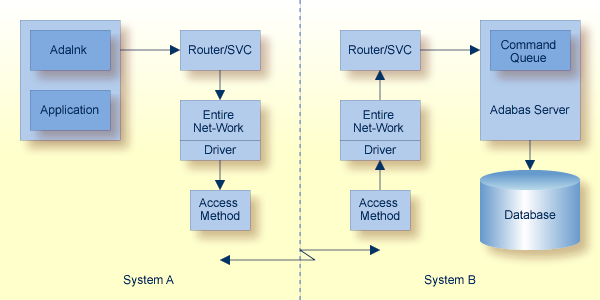
An Entire Net-Work communicator with an appropriate access method line driver is installed on both systems. The two line drivers establish the connection with each other through the appropriate access method services.
Adabas Fastpath can be used to optimize a client query for data from a remote database where the Adabas Fastpath buffer is in the same operating system image as the client. Entire Net-Work makes the location of the database transparent to the optimization process and there are no special installation requirements.
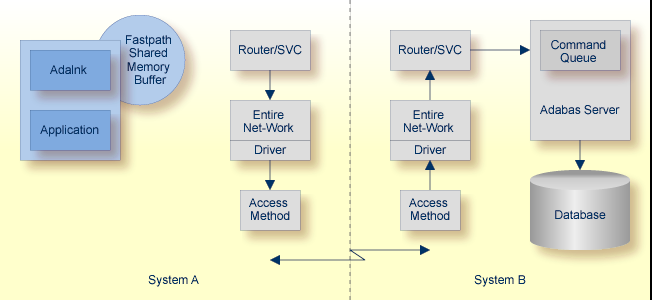
When a command is optimized by Adabas Fastpath (that is, satisfied from the Adabas Fastpath shared memory buffer), the Entire Net-Work communication path is bypassed as well as the Adabas command processing.
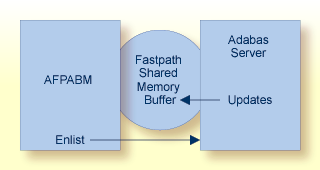
In a single system implementation or a multisystem implementation where the Adabas Fastpath buffer is in the same operating system image as (that is, local to) the updated Adabas server, AFPABM communicates with each Adabas server for which it has any file parameters with update-level sensitivity. When the integrated Adabas Fastpath update component in the Adabas server is alerted to an update, the details are immediately reflected in the local Adabas Fastpath buffer as follows:
For multisystem implementations where the Adabas Fastpath buffer is not local to the updated Adabas server, the Adabas Fastpath update component in the Adabas server signals the remote AFPABM component in order to reflect the update in the remote system as follows:
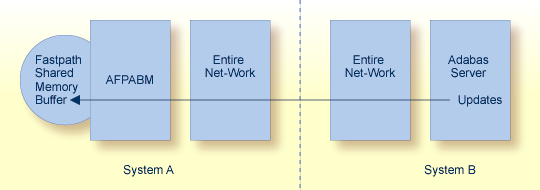
The originating update command is delayed in the Adabas server until the remote AFPABM has received the update signal. Every effort is made by AFPABM to respond immediately, although some delay to the update thread in the Adabas server is inevitable. Other update threads function without delay unless they depend on the updated ISN.
Multiple AFPABM instances may enlist with the same Adabas server, especially in large implementations. In such cases, the update signalling cycle will take longer. You will need to consider the number of updates processed to determine the optimization benefits.