Adabas Review runs in:
local mode in the Adabas address space.
hub mode as a server in its own address space with a client interface in the Adabas address space.
batch mode as a batch job that processes sequential Adabas command log data sets
See the Release Notes for this version of Adabas Review for a matrix of supported Adabas versions and other requirements.
This document covers the following topics:
In local mode, the Adabas Review processor is installed as an extension to ADALOG.
The data collection process is partly accomplished by the Adabas Review processor. The data is collected by providing code (RAOSLOCL) that runs as an extension to ADALOG. Adabas calls this module and passes information about resource usage for each command processed by the Adabas nucleus.
This module, in conjunction with the Adabas Review processor and an intermediate Adabas Review buffer, accumulates and tabulates the Adabas information based on various user-defined data requirements.
The Adabas Review data may be:
displayed in an online environment from the Adabas Review user interface;
printed automatically when the Adabas nucleus terminates; or
downloaded directly to a personal computer (PC) using Entire Connection.
The following graphic shows the Adabas Review data collection process for local mode.
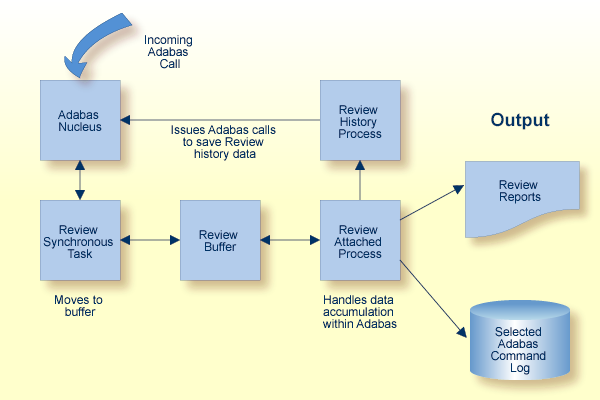
In local mode, Adabas Review job control statements should be added to the Adabas nucleus startup job.
In hub mode, Adabas Review uses a client/server approach to collecting data:
an interface (the client) resides on each Adabas nucleus; and
the hub (the server) resides in its own address space, partition, or region.
The interface uses the existing Adabas interregion communication process: ADALINK, Trans-port, ADASVC (ADARER), and ADAMPM. This process is consistent across the targeted platforms for Adabas Review. If systems are networked correctly, hub mode supports a multiple platform, multiple operating system, Adabas database environment.
In hub mode, Adabas Review job control statements should be added to the Adabas Review hub startup job.
Note:
Trans-port is available only in z/OS environments.
The Adabas Review hub is a centralized data collector and reporting interface that combines proven components of Adabas and Adabas Review.
It handles the data consolidation and reporting functions for monitoring an Adabas database, including usage information related to applications, commands, command response time, I/O activity, buffer efficiency, and others.
The interactive reporting facility allows you to pinpoint problems quickly, providing detailed and summary data about Adabas activities. Specific information about each database is also available.
The centralized collection server has several advantages:
A single hub collects information from multiple Adabas nuclei, Adabas Parallel Services clusters, or Adabas Cluster Services (support for IBM's parallel sysplex environment) clusters.
Because a single hub can support multiple Adabas nuclei, the number of Adabas Review nuclei required to support an enterprise-wide distribution of Adabas nuclei is reduced. This minimizes resource requirements and increases performance.
Isolating the Adabas Review subtask from the Adabas nucleus enhances the performance of the Adabas main task and minimizes the impact of future Adabas releases on the functioning of Adabas Review.
ADAREV, a logic module that manages and supervises the incoming Adabas Review data calls and requests;
REVHUB, a module to establish and maintain the environmental settings for Adabas Review; and
the Adabas Review DB nucleus and subsystems including RAOSAUTO, the autostarted report parameter generation routine, and RAOSHIST, the historical data population routine.
The Adabas Review interface constructs and then transmits the Adabas Review data from the Adabas nucleus to the Adabas Review hub. An Adabas Review interface is integrated with each Adabas nucleus that is monitored.
ADACLX, the Adabas command log extension module that is responsible for acquiring additional information not present in the Adabas command log record; and
ADARVU, which handles the environment conditions for ADACLX and the Adabas API requirements for transmitting the Adabas Review data to the Adabas Review hub.
To maximize performance, the ADARVU module issues an "optimistic" call from an Adabas nucleus to the Adabas Review hub without waiting for a completion or "post" from the hub; ADARVU assumes that the Adabas Review data was successfully passed to the hub.
However, ADARVU does perform an initialization step to ensure that the hub is active prior to any command processing by the Adabas nucleus. If the hub is not active, ADARVU informs you using WTOs or a user exit. If a user exit is used, you are given the option to wait for the hub to be activated, or continue initialization and call the hub only when it is active.
Command log records are normally buffered to reduce the number of calls from the Adabas nucleus to the Adabas Review hub. In low traffic situations, this might lead to a delay of approximately five seconds.
If the communication to the hub results in a non-zero response code (for example response code 151), ADARVU will call user exit 5 if it is available. If a user exit is used, you are given the option to resend the whole buffer (with or without a wait), although parts of the buffer may already be processed. We recommend that you not resend the buffer, but generate a message indicating an error has occurred correct the problem. For more information about user exit 5 read User Exit 5 (Adabas Review Hub Event Handler) in the appropriate Adabas Review installation guide.
On the hub side of the call, the elimination of the cross-memory "post" call enhances performance by reducing the overhead of active communication with the Adabas clients. This allows the hub to remain a passive data collector.
The following graphic shows the major components of the Adabas Review interface (Adabas nucleus address space) and hub (Adabas Review hub address space) in a client/server architecture .
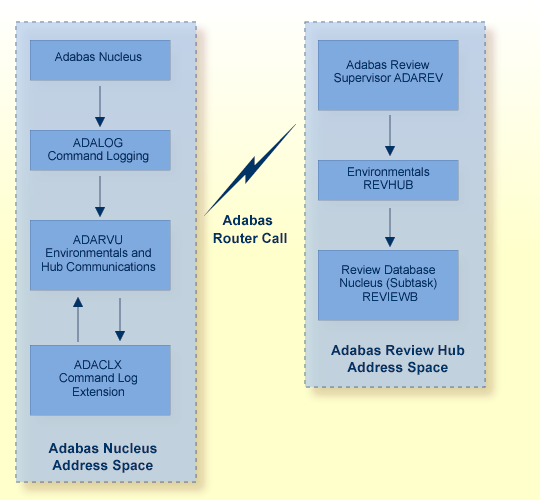
The data collection process is partly accomplished by the hub (server) component REVIEWB, the Adabas Review command log processing routine, which runs as an Adabas Review subtask; that is, a unit of work that the operating system treats as separately detachable.
At initialization, REVIEWB reads any autostarted report definitions the user has defined and collects data according to the reports' criteria. REVIEWB also processes requests to start, view, and purge reports from the Adabas Review online system.
In hub mode, Adabas responds to requests and calls the interface module ADARVU from ADALOG (Adabas's command logging module) if REVIEW=dbid is specified in the Adabas initialization parameters. Adabas passes to ADARVU information about resource usage for each command processed by the Adabas nucleus.
Adabas Review link routine exits are used to pass TP system and Natural information from the user's address space (origin of the Adabas call) to the Adabas address space and, using an extension of the Adabas user buffer, on to ADARVU.
ADARVU queues Adabas command log records received from ADALOG to the Adabas Review hub ( server) through an intermediate REVIEW-BUFFER in the Adabas subtask address space. Note that command log records are examined prior to queuing to determine whether record filtering is active. When filtering is active, only command log records that are filtered are sent to the hub.
See Record Filtering for more information.
REVIEWB processes the records, accumulating and tabulating various data according to the criteria specified in any user-defined reports that are active.
The resulting nucleus statistics may be
displayed in an online environment from the Adabas Review user interface;
saved automatically in an Adabas file called the Adabas Review repository;
printed automatically when the Adabas nucleus terminates; or
downloaded directly to a personal computer (PC) using Entire Connection.
The following graphic shows the Adabas Review data collection process for hub mode. When monitoring multiple databases, Adabas Review allows you to switch from one database to another and provide reports for each.
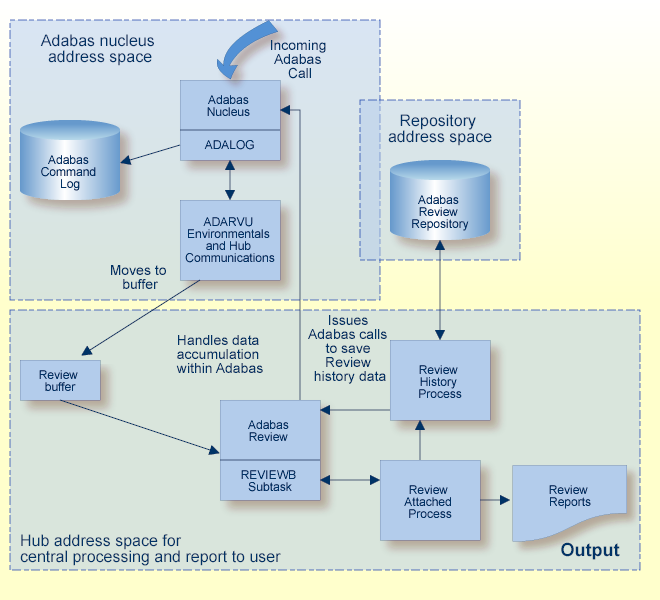
History data collection is controlled by RAOSHIST, the Adabas Review historical data population routine.
RAOSHIST executes as a subtask of Adabas Review. At initialization, RAOSHIST reads the RVUALT data set to determine if there are any historical records from the previous Adabas Review session that should be written to the Adabas Review repository. History records are written to RVUALT if the database on which the Adabas Review repository resides is unavailable during Adabas Review termination.
During normal execution of Adabas Review, REVIEWB is responsible for adding history records generated by detail history reports and by summary history reports that have a history interval.
As a batch job, the Adabas Review command log processing routine REVIEWB processes Adabas command log records from a sequential data set. If you use Adabas dual command logging, you must first use the Adabas utility function ADARES CLCOPY to generate a sequential command log data set suitable for input into Adabas Review.
When Adabas Review executes as a batch job, input report parameters that define the data collection criteria selected by the user are read from statements in the RVUPARM data set or the RVUAUT1/RVUAUT2 data sets. These statements can be generated using the GENCARD statement.
The storage allocated for reports is exactly the same as that for Adabas Review executing in interactive (online) mode. However, since REVIEWB is reading the command log records directly from a sequential file, no REVIEW-BUFFER is allocated.
The Adabas Review repository is an Adabas file used for storing report definitions, historical data, and target definitions. In hub mode, it cannot run in the hub address space.
Depending on the configuration at your site, more than one Adabas Review repository may be associated with your system. For example, if your site is running Adabas Review against more than one database, you may choose to have an Adabas Review repository for each database.
The Review command SETFILE (or SET) may be used to access different Adabas Review repositories and the reports stored on them.
Adabas Review administrators use the user profile system to generate profiles that define access rules for Adabas Review users. Access rules specify the systems or the functions within systems that a particular user is allowed to use.
User profiles may be created for new users, changed for existing users, and purged when no longer required.
A user profile is not required for each user. Adabas Review provides a default profile to allow access for users who do not have a profile defined.
When a user logs on, Adabas Review searches for the user's profile. If one is not found, the default profile is used.
If the default profile is customized so that the access rules meet the needs of the majority of Adabas Review users, the need for individual user profiles can be eliminated.
If a user has access needs that are different from the majority, a user profile can be created to accommodate those needs. Such a profile is generated by customizing a copy of the default profile.
Adabas ADARUN initialization parameters define and start the Adabas operating environment. Different ADARUN parameters are useful to the Adabas nucleus and the Adabas Review hub in different operating environments. For more information about the ADARUN parameters specific for Adabas Review in a given environment, select the appropriate link below: