The hyperdescriptor exits (hyperexits) 1 through 31 (HEX01...HEX31) are required to define the algorithm for user-supplied descriptor values (see the Adabas Utilities Manual documentation ). A hyperexit is called by the ADACMP utility or the Adabas nucleus whenever a hyperdescriptor value is to be generated. ADACMP always uses the hyperdescriptor exit specified in its own ADARUN statement. When the ADAINV utility specifies a hyperdescriptor exit, the exit used is the one specified in the Adabas nucleus' ADARUN statement.
Notes:
This document covers the following topics:
| Parameter | Content |
|---|---|
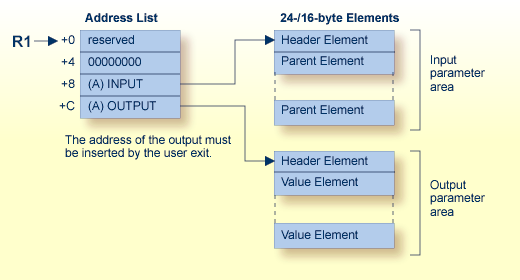
| 0 (R1) | Reserved (must not be changed) |
| 4 (R1) | Fullword of zeros (must not be changed) |
| 8 (R1) | Address of the beginning of the input parameter area. |
| 12 (R1) | Address of the beginning of the output parameter area. This address must be inserted by the user-written program. An output parameter area must always be returned by the user hyperexit. If no values are to be returned, the address will point to a Header Element with a total length that indicates no Value Elements exist. |

| LL | Total length of the input parameter area, including this length field |
| FNR | File number |
| ISN | ISN assigned to the record |
| HN | Name of the hyperdescriptor |
| F | Flag byte:
|
| FN | Name of the parent field |
| L | Length of the value pointed to by VALADDR if the parent field is defined with the FI option. |
| I | Four-byte periodic group index of the parent field. If the parent field is not part of a PE group, these bytes contain zeros. |
| VALADDR | Address of the value of the parent field. The format of the value depends on the options of the fields. If the parent field is defined with the NU (null value suppression) option and the value for this field is suppressed, no input parameter element is created. |
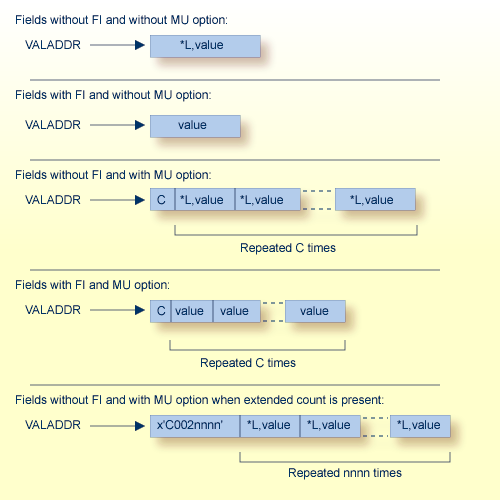
The following examples show formats for the value pointed to by VALADDR for parent fields with combinations of the FI (fixed storage) and MU (multiple-value) options:
where:
| C | A one-byte value representing the MU count. If the MY value is for a file defined with extended MU or PE fields, an extended count may be present. For more details on the extended count, read Identifying MU and PE Occurrences Greater Than 191 in Compressed Records , found in the ADACMP documentation. |
| *L | A hexadecimal value length, including this one- or two-byte length value. For lengths from 1 through 127, only a single byte is required. For lengths ranging 128 to 255, two bytes are needed: the first byte is set to X`80', and the second byte is set to the actual length value (see the following example table): |
| Length | Byte 1 | Byte 2 |
|---|---|---|
| L=127: | x`7F' | (x`80') |
| L=128: | x`80' | x`80' |
| L=255: | x`80' | x`FF' |
This area must be allocated and filled within the hyperdescriptor user exit. The address of this area must be placed into the second position of the main parameter area.
This area consists of a 8-byte header followed by the generated hyperdescriptor values in compressed format.

| LL | Total length of the output parameter area, including this length field. If no values are returned, the total length is set to the length of the Header Element. |
| 00 | Reserved space. This must be set to zeros. |
| RC | Return code. The hyperexit may set a non-zero value here to indicate the call is rejected; a value of "16" is recommended. If this field is non-zero, the call will fail with response code 79. |
| ISN | The ISN to be assigned to the descriptor values. If the original ISN is to be changed, the new ISN must be inserted here. If these four bytes contain zero on return to the Adabas nucleus, the original ISN is used. This is a four-byte binary value. |
Note:
If the hyperexit returns an ISN in the ISN field of the header
element, the file must be defined with USERISN=YES to prevent ISN reassignment
when the file is later reloaded.
| L | Length of the following value, including this length byte. The maximum length depends on the format in use for the hyperdescriptor. |
| Value | The descriptor value to be inserted into the index. The value must follow the rules in effect for the format assigned to this hyperdescriptor. If the hyperdescriptor is defined with the PE option, one byte containing the one-byte PE index must immediately follow the value and be included in length L. If the hyperdescriptor defined with the PE option is for a file defined with extended MU or PE fields, two bytes containing the two-byte PE index must immediately follow the value and be included in length L. The nucleus checks values of packed or numeric format for validity. Valid signs for packed fields are A,C,E,F (positive) and B,D (negative). The nucleus changes all signs to F or D. |
Examples:
| L | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 04 | R E D | |
| 06 | B L U E02 | where X'02' is a PE index |
| 03 | 123F | packed 123 |
| 04 | 123F01 | packed 123 in PE group with index 1 |
| 07 | B L U E0002 | where X'0002' is a PE index for a file defined with extended MU or PE fields |
| 05 | 123F010A | packed 123 in extended PE group with index 266 |
The NU (null value) option is possible for the hyperdescriptor or parent fields. The possible combinations are as follows:
The hyperdescriptor is not NU:
The parent field is not NU and the value is null, the hyperexit is called and the null value is passed.
The parent field is NU and the value is null, the hyperexit is called and no input parameter element is created for this parent field.
All parent fields are NU and all values are null, the hyperexit is called and no input parameter element is created for any parent field.
The hyperdescriptor is NU:
The parent field is not NU and the value is null, the hyperexit is called and the null value is passed.
The parent field is NU and its value is null, the hyperexit is called and no input parameter element is created for this parent field.
All parent fields are NU and all values are null, the hyperexit is not called.
During Adabas nucleus or ADACMP startup, each loaded hyperexit is called with an initialization call. The main parameter area must be used as documented. The third parameter address will point to an input parameter area with a header length indicating that no values follow. The flag byte will be set to x'80' to indicate the initialization call. Upon return, the hyperexit must set the fourth parameter address to an output parameter area with a header length indicating that no values are returned.
The Hyperexit Stub is provided to allow earlier hyperexits to use the Adabas 8 parameter list without change. The Hyperexit Stub is intended as a temporary solution for those customers who do not wish to immediately update their hyperexits to use the new parameter areas. The Hyperexit Stub will not function for files that are defined with extended MU or PE fields; a response code will be given when the Hyperexit Stub is called for such files. Hyperexits linked with the Hyperexit Stub may be used with earlier versions of Adabas, however, the Hyperexit Stub must not be used with hyperexits that use the Adabas 8 parameters.
Sample job LNKHEX8 in the JOBS data set provides an example for linking the Hyperexit Stub to your hyperexit.
In z/VM environments, use the following procedure to build your hyperexit with the hyperexit stub:
Edit the file INPUT TEXT provided on the distribution tape. On the third line (NAME HEXnnMOD), change the name to your hyperexit. The same name should be set in the ADARUN HEXnn parameter. Do not change any other lines. Save the file.
INCLUDE LIBDEF(HEXV87,HEXOLD) INCLUDE TXTDEF NAME HEXnnMOD
Generate the hyperexit with the following commands:
FILEDEF LIBDEF DISK ADAV813 TXTLIB
x (where x is the
filemode containing ADAV813 TXTLIB)
FILEDEF TXTDEF DISK HEXnn TEXT
x (where HEXnn is
your hyperexit, and x is the filemode where it
resides)
LKED INPUT (LIBE HEXnn)
(where HEXnn is the name of the new LOADLIB
containing the hyperexit)
Before starting the Adabas nucleus, specify GLOBAL LOADLIB
HEXnn.