This section contains operator commands for Entire Net-Work, and for its XCF line driver.
Although Entire Net-Work operates automatically, there are operator commands available during execution to display or modify the status of the network and control the local Entire Net-Work node.
In OS/390 environments, the following operator commands are used:
MODIFY F
STOP P
The STOP (or P) command serves as an alternative to the NETEND command and terminates Entire Net-Work. Its synonyms are described as part of the following example:
Entering the following long form MODIFY commands results in the following status displays (assuming that NETWK is the name of the started task running Entire Net-Work):
MODIFY NETWK,D STATS NET0090I: BUFFER USAGE STATISTICS: NET0091I: ASYNCH. BUFFERS: 000016 (= 24.2 %) OF 000064 K USED NET0091I: LONG TERM BUFFERS: 000000 (= 0.4 %) OF 000064 K USED NET0091I: SHORT TERM BUFFERS: 000000 (= 6.1 %) OF 001025 K USED NET0091I: ATTACHED BUFFERS: 000000 (= 11.9 %) OF 000080 K USED NET0091I: REQUEST QUEUE: 000000 (= 6.0 %) OF 000050 K USED NET0087I: 0000010847 REQUESTS FROM LOCAL RQ
The following two commands are equivalent ways to terminate the Entire Net-Work session:
F NETWK,NETEND P NETWK
The Entire Net-Work commands described in this section are similar to Adabas operator commands. The underlined portion of the command is the minimum abbreviation.
Entire Net-Work line drivers have the ability to process operator commands that are directed to a specific link or directly to the driver. The operator commands that are specific to the XCF line driver are described in the section XCF Line Driver Commands.
This document covers the following topics:
The following table summarizes the Entire Net-Work operator commands for OS/390:
| Command | Argument | Action |
|---|---|---|
| ADAEND | Terminate Entire Net-Work session. | |
| CLOSE | driver | Disconnect all links of a driver, then close the driver. |
| CLOSE NETPRNT | Close the NETPRNT file and route all trace and snap output to DDPRINT. | |
| CONNECT | link | Reconnect a link after a disconnect or handshake error. |
| DEFINE | link | Dynamically define a new link. |
| DISABLE | link | Disable a link (link cannot accept connects). |
| DISCONNECT | link | Disconnect a link. |
| DISPLAY | parameter | Display link, nodes, targets, paths, or statistics. |
| DUMP | Snap data areas, then terminate the Entire Net-Work session. | |
| ENABLE | link | Enable a link (the link can accept connects). |
| END | Terminate Entire Net-Work session. | |
| FORCE | node | Broadcast a "node down" message. |
| HALT | Terminate Entire Net-Work session. | |
| HELP | List available operator commands. | |
| NETEND | Terminate Entire Net-Work session. | |
| OPEN | driver | Reopen a driver after a close or access method failure. |
| OPEN NETPRNT | Open the NETPRNT file and route all trace and snap output to the NETPRNT file. | |
| PROBE | node | Send a probe message to a node. |
| RESUME | link | Resume sending messages using this link. |
| SET | parameter | Change the values of Entire Net-Work parameters.
Note: |
| SNAP | Snap data areas to DDPRINT. | |
| START | driver | Restart driver (then connect all links of the driver). |
| STOP | taskid | Terminate Entire Net-Work session. |
| SUSPEND | link | Stop sending messages on this link. |
| TERMINATE | Terminate Entire Net-Work session. |

Any one of the above commands can be used to terminate an Entire Net-Work session normally. The STOP operator command (for example, STOP taskid or P taskid) can be used in the OS/390 environment.
Once the termination command has been accepted by Entire Net-Work, no more requests are selected from the request queue. Message NET0999 is displayed on the operator console confirming that normal termination procedures have been started.
Note:
The DUMP command also ends Entire
Net-Work operation after performing a snap dump of pertinent data areas.

Terminate all activities of the line driver by disconnecting and closing all links related to the driver, then closing the driver itself.
The driver name must be the same as was specified on the XCF DRIVER statement (that is, either XCF or XCFD). See section XCF DRIVER Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation for more information.
The effect of this command can be reversed by issuing the OPEN or START command for the driver, and CONNECT commands for the links (as appropriate).

Close the NETPRNT file and route all trace and snap output to the DDPRINT file. When the NETPRNT file is closed, the dataset can be copied for sending to Software AG support without shutting down Entire Net-Work. The file must be allocated SHR. This command cannot be abbreviated.

Attempt to connect link 'linkname'. The link name specified must match that used on the LINK statement. If the link was disconnected after a "handshaking" conflict, the CONNECT command can be used to retry the procedure. If the link is disabled, the CONNECT command can be used to enable it.

Defines a link during Entire Net-Work operation. The link statement must adhere to the format described in section XCF LINK Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation. The following example applies to the Entire Net-Work XCF line driver:
DEFINE LINK SYS01 XCF MEMBER=NODE01,PSTATS=Y,- RSTATS=N,STATINT=3600,TRACESIZ=4096
The LIKE linkname clause can be used instead of the LINK statement to define a link by copying the parameters specified for a previously defined link. For example:
DEFINE LINK SYS02 LIKE SYS01
Note:
DEFINE LINK is permitted only when
DEFINE=Y is specified on the NODE statement.

Instructs the specified link not to accept any connections from other Entire Net-Work nodes. If the link is connected, it is disconnected and then disabled.

Disconnect the link 'linkname' connected to this node. The link name specified must be the same as that used on the LINK statement.

Displays current information about the specified network component. Only one component type (link, node, path, or target) can be specified in a single DISPLAY command. The information is displayed in the form of Entire Net-Work messages. Refer to the Entire Net-Work Messages and Codes documentation for information about specific messages.
The optional second parameter serves to qualify the display request, thereby limiting the information displayed. At the same time, additional information is displayed for qualified DISPLAY LINK or DISPLAY NODES requests.
The possible qualifier values and their meanings depend on the type of request. A link name, node name, or (numeric) target ID may be specified. Alternatively, a string ending in a "wild card" character (*) may be used to indicate all links or nodes whose names start with the specified string. The asterisk (* ) alone may be used to produce a display of all links or nodes, but additional information is shown only for qualified display requests.
The following is an example of DISPLAY ALINKS output. DISPLAY ALINKS lists currently active links only:
F NETWK,D AL NET0120I: VTAM LINK LNKE TO NODE ENODE STAT=ACTIVE NET0120I: VTAM LINK LNKA TO NODE ANODE STAT=ACTIVE
The following is an example of DISPLAY LINKS output:
F NETWK,D L NET0120I: VTAM LINK LNKALS TO NODE ALSNODE STAT=DISC NET0120I: VTAM LINK LNKE TO NODE ENODE STAT=ACTIVE NET0120I: VTAM LINK LNKA TO NODE ANODE STAT=ACTIVE NET0120I: VTAM LINK LNKVM TO NODE UNKNOWN STAT=OPEN
The following is an example of DISPLAY LINKS output for all links whose names begin with "TO":
F NET1,D L TO* NET0120I: VTAM LINK TOSIX TO NODE SIX STAT=ACTIVE NET0112I: 2 MSGS; 2 TR.BLKS NET0120I: VTAM LINK TOTWO TO NODE TWO STAT=ACTIVE NET0112I: 3 MSGS; 3 TR.BLKS NET0120I: VTAM LINK TONINE TO NODE UNKNOWN STAT=CONSTA NET0112I: 0 MSGS; 0 TR.BLKS
The following is an example of DISPLAY NODES output:
F NETWK,D N NET0122I: NODE FNODE (50752) LOCAL NET0122I: NODE ALSNODE (54080) DIST 000040 VIA LINK LNKE NET0122I: NODE ANODE (49472) DIST 000020 VIA LINK LNKA NET0122I: NODE ENODE (50496) DIST 000020 VIA LINK LNKE
A qualifier is used in the following example:
F NETWK,D N A* NET0122I: NODE ALSNODE (54080) DIST 000040 VIA LINK LNKE NET0123I: TARGETS: 00025 00171 00194 00175 00173 00018 00009 NET0123I: TARGETS: 00177 NET0122I: NODE ANODE (49472) DIST 000020 VIA LINK LNKA NET0123I: TARGETS: 00125 00192
The following is an example of DISPLAY PATHS output:
F NETWK,D P NET0122I: NODE ALSNODE (54080) DIST 000080 (001) VIA LINK LNKA NET0122I: NODE ALSNODE (54080) DIST 000040 (002) VIA LINK LNKE NET0122I: NODE ANODE (49472) DIST 000020 (001) VIA LINK LNKA NET0122I: NODE ANODE (49472) DIST 000040 (002) VIA LINK LNKE NET0122I: NODE ENODE (50496) DIST 000040 (002) VIA LINK LNKA NET0122I: NODE ENODE (50496) DIST 000020 (001) VIA LINK LNKE
The DISPLAY STATS command produces the same type of information found in the statistics displayed at the end of an Entire Net-Work session. A qualifier parameter, if given, would have no effect. The buffer usage statistics displayed depend on the operating system being used.
The following is an example of DISPLAY STATS output for an OS/390 system. It includes a NETB001I and a NETB009I for each active buffer pool, a set of NETB008I, NETB010I, and NETB012I for each subpool within the buffer pools, and a NETB013I for each operator command issued.
F NETWK,D STATS NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB001I: Statistics For Buffer Pool COMN Loc = ANY NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB008I: Req =( 13, 0, 10, 0) NETB010I: ELM =( 512, 512, 512, 512), Sz = 512 B NETB011I: Str =( 256, 256, 254, 252 ) K NETB012I: Exp =( 0, 1, 0, 0) NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB008I: Req =( 1, 0, 0, 0) NETB010I: Elm =( 10, 10, 10, 2), Sz = 1 K NETB011I: Str =( 15, 15, 13, 13) K NETB012I: Exp =( 0, 1, 0, 0) NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB008I: Req =( 1, 0, 0, 0) NETB010I: Elm =( 1, 1, 1, 1), Sz = 14K NETB011I: Str =( 14, 14, 0, 0) K NETB012I: Exp =( 0, 1, 0, 0) NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB009I: High Allc= 285 Curr Allc = 285 Curr Avail = 267 K NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB001I: Statistics For Buffer Pool PGFX Loc = ANY NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB008I: Req =( 0, 0, 0, 0) NETB010I: Elm =( 64, 64, 64, 0), Sz = 4K NETB011I: Str =( 256, 256, 256, 256) K NETB012I: Exp =( 0, 0, 0, 0) NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB009I: High Allc= 256 Curr Allc = 256 Curr Avail = 256 K NETB000I: ---------------------------------------------------------------- NETB013I: Combined Buffer Pools Size 541 K NETB000I: ----------------------------------------------------------------
The following is an example of DISPLAY TARGETS output:
F NETWK,D T NET0124I: TARGET 09777 (C-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ALSNODE NET0124I: TARGET 00009 (I-T) ACTIVE ON NODE ALSNODE NET0124I: TARGET 02048 (L-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ANODE NET0124I: TARGET 00237 (I-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ANODE NET0124I: TARGET 00238 (I-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ANODE NET0124I: TARGET 09888 (C-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ANODE NET0124I: TARGET 00234 (I-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ANODE NET0124I: TARGET 55769 (C-N) ACTIVE ON NODE ANODE
The DISPLAY ZAPS command lists, for each Entire Net-Work module, its name, assembly date, system maintenance level, and ZAP level. If ZAPs were applied after initial shipment, their numbers are listed as "Additional ZAPs". The following is an excerpt from a DISPLAY ZAPS example:
F NETWK,D Z NET0037I: NETCLF (1998/11/10 SM=0001) ZAP LEVEL 0000

Issue a snap dump, then end the Entire Net-Work session. DUMP is equivalent to the SNAP command followed by an ADAEND (or synonymous) command.

Revokes a previously entered DISABLE command. The specified link is instructed to accept incoming connect requests. Enabling a disconnected link does not connect the link.

Broadcasts a control message through the network to notify all Entire Net-Work nodes that the specified node is no longer available. This command is provided for diagnosis and exception handling, and should be used only on the advice of your Software AG technical support representative.

Lists the available Entire Net-Work operator commands with a short explanation of their function.

Reopen an installed and defined line driver that was stopped due to an access method or other network or system failure, or by the CLOSE operator command.
The driver name must be the same as was specified on the XCF DRIVER statement (that is, either XCF or XCFD). See section XCF DRIVER Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation for more information.
Note that this command is currently a synonym for the START command. See the explanation in section XCF DRIVER Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation for more information.

Open the NETPRNT file and route all trace and snap output to NETPRNT. This command is necessary only after a CLOSE NETPRNT command has been used. It opens the NETPRNT file when Entire Net-Work is initialized. If the file is allocated SHR or OLD it will be erased when opened. This command cannot be abbreviated.

The PROBE command verifies that the specified node is available and can be reached. Entire Net-Work issues internal probe commands for the same purpose during normal operation. PROBE routes an internal message to the specified node and back. If the node cannot be reached, this information is sent to all active nodes, updating the node status.
The optional second parameter specifies that nnnn bytes of random user data (64512 bytes maximum) are to be appended to the actual probe message. The exact length of the message sent can be calculated as follows:
70 + (nodestack-size) + nnnn
where 'nodestack-size' is twice the number specified by the
NODE statement parameter MAXPATH,
rounded up to the next multiple of 4. For example, if
MAXPATH=4 (the default value), the following command
results in a message of length 1078:
PROBE nodename 1000
The result of the operation is displayed on the operator console, as shown in the following example:
F NET1,PROBE TWO NET0136I: PROBE MESSAGE SENT NET0135I: PROBE FOR NODE TWO (0001.711 SEC) NET0120I: NODE TWO (62194) DIST 000030 VIA LINK TOFIVE NET0140I: VERSION 5.7.1 (1999/11/10)

Revokes a SUSPEND command for the specified link. The link's status changes to "active" and the link resumes sending queued messages.

The SET command can be used to change Entire Net-Work parameter settings dynamically without interrupting network operations. Multiple parameters can be specified with one SET command.
The SET command keyword itself may be omitted. For example:
F NODEA,SET CQTIMER=180, TRACE=OFF
is equivalent to
F NODEA,CQTIMER=180, TRACE=OFF
The parameters allowed for the SET command are a subset of those defined on the Entire Net-Work NODE statement. They are as indicated below:

The approximate waiting time, in seconds, allowed for a user or application to retrieve command results with a router 16-call before timeout occurs. For more information, see the CQTIMER parameter description in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

The storage areas to be included in a dump when Entire Net-Work terminates abnormally. The information is printed to the NETPRNT file if it is open; otherwise, it is printed to the DDPRINT file. SET DUMP can be used to reduce the amount of output generated during an ABEND, especially on large Entire Net-Work systems. This command cannot be abbreviated.
In general, the default value of ALL should be used so that all diagnostic information is available to Software AG support.
Multiple values can be specified, separated by commas and surrounded by parentheses. For example:
SET DUMP = (BLOCKS, TRACETAB, FORMAT)
If conflicting values are specified, the last value specified is used. In the following, for example, the value used is NONE:
SET DUMP = (BLOCKS, TRACETAB, NONE)
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ALL | All storage areas are dumped. This is the default value. |
| NONE | No storage areas are dumped. |
| BLOCKS | The major control blocks are dumped. |
| TRACETAB | The internal trace table is dumped. |
| BUFFERS | All internal buffer areas are dumped. |
| LINKAREA | All storage areas related to a driver and link are dumped. |
| FORMAT | The driver and link trace tables are formatted. |

Regulates control flow and logging of selected data areas to the printer dataset. For more information, refer to the LOG parameter description in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

The maximum path link, specified in number of links, that a message from users on this node is expected to travel. For more information, refer to the MAXPATH parameter description in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

The message format of console messages and DDPRINT output. For more information, see the MSGFORM parameter in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

The time, in seconds, that this node is to wait for a reply to a user request before timing out. For more information, refer to the REPLYTIM parameter description in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

Sets the trace control parameters for program traces. For more information, see the TRACE statement parameters in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

Controls whether messages are issued in uppercase or mixed case. For more information, see the UCMSG parameter in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

Allows or disallows multiple links to an adjacent Entire Net-Work node. For more information, see the ULINK parameter in the Parameters and Parameter Statements documentation.

Issue a snap dump of selected data areas to the DDPRINT file and continue processing.
Note:
Under certain circumstances, a snap dump is performed internally at
either normal or abnormal session end.
The optional parameters are used to snap one or more specific data areas:
| Parameter | Area |
|---|---|
| BPH | Buffer pool headers |
| CQ | Command queue |
| CURRMSG | Message that Entire Net-Work mainline is currently working on |
| MAIN | Header of mainline module |
| MYBLK | Central control block |
| TRACE | Internal trace table. |
| UBQ | User buffer queue (currently active Adabas commands) |

Restart the installed line driver that was stopped due to an access method or other network or system failure, or by the CLOSE operator command.
The driver name must be the same as was specified on the XCF DRIVER statement (that is, either XCF or XCFD). See section XCF DRIVER Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation for more information.
The START command is a synonym for the OPEN command.

Instructs the specified link to stop sending messages. However, Entire Net-Work can still queue messages on this link. The SUSPEND command is valid only if the link is active.
The Entire Net-Work XCF line driver has the ability to process operator commands that are directed to a specific link, to all links, or directly to the driver.
The XCF line driver operator commands have the following format:

where
'XCFD' tells Entire Net-Work that the command is destined for the XCF line driver. See section XCF DRIVER Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation for more information.
'target' identifies the target of the command to XCF and has the following format:
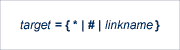
XCF line driver operator commands depend on whether the target is the driver of one or more links. Specify
"*" if the target is all links.
"#" if the target is the driver itself.
the link name if the target is a specific link.
'cmd1 cmd2 .... cmdx' are the operator commands to be issued.
Multiple commands can be specified in a single command statement.
When the ALTER
command is specified, it must be the last command in the
statement, because everything following the ALTER
command is treated as a DRIVER or
LINK statement parameter.
The Entire Net-Work XCF line driver supports the commands listed in the following table. All commands are available for both link and driver targets. The underlined portion of the command is the minimum abbreviation.
| Command | Action |
|---|---|
| ALTER | Dynamically changes the driver or link configuration. |
| HELP | Lists available operator commands. |
| RESET | Resets all statistics for the driver or link. |
| SHOW | Displays parameter settings for the driver or link. |
| SNAP | For driver targets, snaps driver-specific data areas. For link targets, snaps all control blocks specific to the link. |
| STATS | For driver targets, displays/prints driver statistics immediately. For link targets, causes the immediate printing of statistics. |
| TRACE | For driver targets, formats and prints the driver-specific trace table. For link targets, prints the link-specific trace table. |

Dynamically changes the driver or link configuration. The ALTER command is followed by the driver or link configuration parameters to be altered, as appropriate. The driver configuration parameters are the same as those specified in the DRIVER statement (see the section XCF DRIVER Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation); the link configuration parameters are the same as those specified on the LINK statement (see the section XCF LINK Statement in the Parameter and Parameter Statements documentation).
For example:
| driver target: |
XCFD # ALTER ACCEPTUI=Y,MAXRU=8A |
| link target: |
XCFD linkname ALTER PSTAT=Y |

Lists all the commands available to display or alter the XCF driver or an XCF link.

Resets all statistics for the XCF driver or link target. Statistics are printed only if the STATS command precedes the RESET command.

Causes the immediate printing of the current driver or link parameter settings.

Causes all driver- or link-specific control blocks and the driver- or link-specific trace table to be snapped (printed in hexadecimal). Entire Net-Work-specific control blocks are not snapped.
For driver targets, link-specific control blocks are not snapped.
For link targets, driver-specific control blocks are not snapped.

Causes the immediate printing of statistics and restarts the statistics interval. To print and reset statistics, specify RESET immediately after the STATS command.
For example:
| driver target: |
XCFD # RESET |
| link target: |
XCFD linkname STATS RESET |

Causes the driver- or link-specific trace table to be formatted and printed. The trace table is also formatted and printed automatically when the SNAP command is processed.