This document describes ADASAF operations.
ADASAF has three main components:
The ADASAF main module, which operates in each secured Adabas address space
Router extensions, which are linked with the Adabas SVC
Online administration and monitoring system, which is a component of the Adabas Online System
As shown in the graphic below, all traffic between the database users and Adabas is controlled by the Adabas router. When ADASAF is installed, the ADASAF component attached to the Adabas router controls all access to the Adabas nucleus.
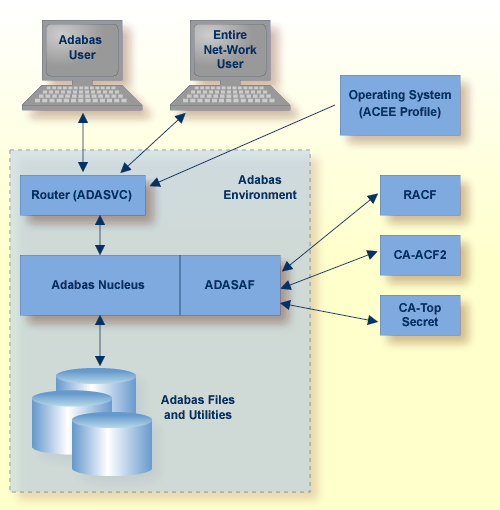
All users must log on to their system using their Logon ID, usually a user name or code. Through the operating system or TP monitor, the installed security package checks the authorization of the Logon ID.
When calls are from a remote workstation or non-IBM platform, the Logon ID and logon password must be given to ADASAF using a remote logon procedure, as described in the section Logging On to a Database. As an alternative to the remote logon procedure, you may configure ADASAF to use the node name or link name of the remote user as the SAF ID. Obviously, these node or link names must be defined as users in the external security system, with the appropriate access rights to Adabas resources.
For Adabas, the router contains a security exit that extracts the user's Logon ID from the ACEE for the user. Even Adabas itself cannot be started unless the user starting the nucleus has proper authority. Through the SAF interface, ADASAF requests the proper authority from the external security packages whenever one of the following events occurs:
A nucleus or utility begins operation;
A user logs on to Adabas;
A user issues an Adabas call;
A user logs off Adabas;
A user issues an Adabas operator command from an MVS console.
When starting an Adabas nucleus, utility or single-user mode batch job, ADARUN calls ADASAF, which checks that the starting user has access to the appropriate resource. The resource name has the format:
pppdbid.SVCsvc
where
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ppp | Represents the last three characters of the program name
specified by the ADARUN PROG= parameter. For example,
NUC for a nucleus, CMP for the ADACMP utility or USR for a single-user mode
batch job.
|
| dbid | Specifies the Adabas Database ID in the selected format (3 or 5
digits with leading zeroes, or without leading zeroes). See the configuration
parameter DBFLEN
for more information.
|
| . | Optional delimiter character, depending on the setting of the
DELIM
parameter.
|
| SVCsvc | The characters SVC followed by the 3-digit decimal number of the Adabas SVC used by this database. |
When starting a nucleus, ADASAF uses the access level to determine whether to run in warn mode (that is, violations are logged, but the access is still allowed) or fail mode (violations result in failure, for example response code 200). If the starting user has only read access to the resource, ADASAF runs in warn mode. If the starting user has update access, ADASAF runs in fail mode.
If the starting user has no access to the resource, or the resource has not been defined, the nucleus abends with a U0042. For utilities, ADASAF requires read access to the appropriate resource. If the starting user does not have read access, or the resource has not been defined, the utility abends with a U0042.
The following Adabas resource name value is for starting the Adabas nucleus for database 1, which runs under SVC 237 (all possible entity constructions are shown):
| Resource Name | Values for DELIM and DBFLEN Configuration Parameters |
|---|---|
ENTITY=NUC001SVC237
|
DELIM= N, DBFLEN=0 |
ENTITY=NUC001.SVC237
|
DELIM= Y, DBFLEN=0 |
ENTITY=NUC00001SVC237
|
DELIM= N, DBFLEN=1 |
ENTITY=NUC00001.SVC237
|
DELIM= Y, DBFLEN=1
|
ENTITY=NUC1SVC237 |
DELIM= N, DBFLEN=2 |
ENTITY=NUC1.SVC237 |
DELIM= Y, DBFLEN=2 |
Note:
Each utility program requires a definition in the external security
database.
Normally, logging on to a database is done using an Adabas
OP command. However, not all applications use an
explicit OP command. ADASAF does not make any
security check until the user actually attempts to access or update a file, at
which point the user's identity will be authenticated.
If one of the non-activity timeout limits expires, the logon must again be validated, just as when logging on to Adabas for the first time.
The logon from a remote workstation client comprises two phases.
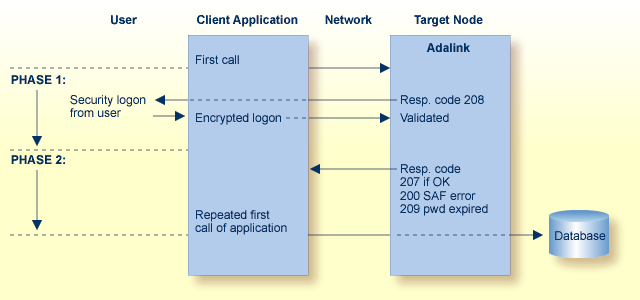
During the initial request from the client program, ADASAF checks to ensure that the user is allowed to log on. The Adabas link routine, which actually performs the check, requires that the client send a Logon ID and security package password to the target.
When the initial command is sent from the client, ADASAF at first rejects the command with response code 208 (start of phase 1). This informs the client that an encrypted Logon ID and password are needed at the target for verification. See the section ADASAF User Exits for more information.
The encrypted Logon ID and password are then sent by the client and validated by the target, and the target returns response code 207 indicating successful completion (start of phase 2). If the duration of phase 1 is more than 60 seconds, a security violation occurs. The original user call is then sent by the client link routine to the database, where the user request is executed.
The Logon ID and password are prompted by the Adabas link routine included in the Entire Net-Work running on the supported platforms.
Entire Net-Work is a prerequisite for ADASAF workstation support. For more information, see the related Entire Net-Work documentation.
As an alternative to Remote Workstation Logon, you can configure ADASAF
to use either the Entire Net-Work node or link name of the remote user as the
SAF Logon ID. This may be useful when the issuer of the remote calls cannot
prompt for a User ID and password (for example, if it is a server rather than a
client). For more information, see the description of the
REMOTE
parameter.
If multiple ADASAF-secured targets are being controlled and these targets reside on different physical machines or nodes, each target node must have the same Logon ID and password assignment per user as every other target node.
When users log off a database, they may or may not issue an explicit
CL command. By default, a close command indicates the
end of ADASAF validity for that user and the user is logged off the security
system. If the user again logs on to Adabas, the user's validity and access
rights are checked again, as though the user were logging on for the first
time.
However, in databases where users have many short-lived sessions (for example, control databases or system file databases), this imposes a considerable overhead on the security system. To log a user on generally involves reading and updating security information and building up the cached security checks anew.
To avoid these overheads, you can instruct ADASAF, via the
LOGOFF parameter, to log users off only when they time
out (or are stopped) in Adabas, or never to log users off (with the exception
that, if ADASAF needs to reclaim memory, it will log off the oldest inactive
user).
On the other hand, if a user's security profile changes, ADASAF will
continue to use the old profile until the user times out or is stopped. So, if
you choose LOGOFF=TIMEOUT and a user's profile changes,
you should stop the user via the STOPU operator
command or Adabas Basic Services to bring the new profile into effect. If you
choose LOGOFF=NEVER and a user's profile changes, use
ADASAF Online Services to forcibly log the user off from the security
system.
ADASAF recognizes three categories of Adabas direct call commands:
Data access commands (Lx,
Sx and HI)
Data update commands (Ax,
Ex and Nx)
Transaction data commands
The equivalent categories of Natural commands are
Data access commands (READ,
HISTOGRAM, FIND)
Data update commands (UPDATE,
DELETE, STORE)
Transaction data commands (END TRANSACTION
with operand1, GET TRANSACTION DATA, generated
OP and CL commands with
option 2 set to E). For more information, see the description of the
ETDATA
parameter.
Only these types of calls have significance for ADASAF and the related
security package. ADASAF recognizes and classifies all database calls according
to one of the command categories described above and performs the authorization
check appropriate to the command category (that is,
ATTR=READ for access commands and
ATTR=UPDATE for update commands).
The entity constructed for a command check takes one of the following formats:
| lvldbidFILnnnnn | if DELIM=N
|
| CMDdbid.FILnnnnn | if DELIM=Y
|
where
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| lvl | is the required access level (ACC for access commands and UPD for update) |
| dbid | represents the Database ID, which is specified in the format
selected by the DBFLEN parameter.
|
| nnnnn | represents the file number, which is specified in the format
selected by the DBFLEN parameter.
|
For example, assuming that DELIM=Y and
DBFLEN=1 (5 digits, with leading zeroes), a user who
issues a DELETE against database 1, file 456, must
have update access to the resource CMD00001.FIL00456.
If the security package does not recognize the user or entity being validated, or the user does not have sufficient access authority, ADASAF returns the following response code to the user:
200 when running in fail mode. Application programs that operate on an ADASAF-protected nucleus must check for a non-zero response code
Zero (0) when running in warn mode
In either case, security violations can optionally be logged in the nucleus DDPRINT or SAFPRINT output.
At its simplest, ADASAF validates that a user has the necessary authority to access or modify Adabas files. However, additional levels of security are available to protect inadvertent or unauthorized data access.
This is known as cross-level checking and allows both the user's and the job's access permissions to be verified. For example, users may be given access to production data but only when they access it from a production TP monitor or batch job.
To achieve this level of protection, ADASAF performs two security checks against the same resource profile (CMD00001.FIL00456 in the example above), but for different resource classes:
the user's User ID is checked against the resource in the class
defined by the DBCLASS
parameter
the originating job's User ID is checked against the resource in the
class defined by the NWCLASS
parameter
If either check fails, the Adabas command is rejected with response 200.
Set XLEVEL to
0: when users’ access rights are not dependent on which environment (job) the user runs in
1: when certain jobs (for example, test TP monitors or TSO users) are not allowed to access this database
2: when certain jobs (for example, test TP monitors or TSO users) are only allowed to access some files on this database
3: when different users have different access requirements depending on which job they are running in
The following is an example of using XLEVEL=2.
Assume that user ABC is allowed to update file 456 on database 1 from production CICS but not from TSO; and that user XYZ is allowed to update file 456 on database 1 from production CICS and also from TSO; and that production CICS runs under User ID PCICS.
This would require the definition of the profile CMD00001.FIL00456 in
both the DBCLASS and NWCLASS
resource classes and granting these permissions
(DBCLASS=ADASEC and
NWCLASS=XLVADA):
| User | Class | Profile Name | Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC | ADASEC | CMD00001.FIL00456 | Read, Update |
| ABC | XLVADA | CMD00001.FIL00456 | None |
| PCICS | ADASEC | CMD00001.FIL00456 | None |
| PCICS | XLVADA | CMD00001.FIL00456 | Read, Update |
| XYZ | ADASEC | CMD00001.FIL00456 | Read, Update |
| XYZ | XLVADA | CMD00001.FIL00456 | Read, Update |
ADASAF performs the following checks:
ABC accesses file 456 from production CICS:
Does ABC (the individual user) have access to resource ADASEC /CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
Does PCICS (the originating job's user) have access to resource XLVADA /CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
The access is allowed.
ABC accesses file 456 from TSO:
Does ABC (the individual user) have access to resource ADASEC /CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
Does ABC (the originating job's user) have access to resource XLVADA /CMD00001.FIL00456? No.
The access is rejected and the command receives response 200.
XYZ accesses file 456 from TSO
Does XYZ (the individual user) have access to resource ADASEC /CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
Does XYZ (the originating job's user) have access to resource XLVADA /CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
The access is allowed.
In this way the database resources are protected not only for individuals but also for jobs. A user may only access allowed resources from jobs which also have the necessary access to those resources.
However, suppose the requirement is more complicated:
ABC is allowed to update file 456 on database 1 from production CICS but not from TSO; and user XYZ is allowed to access file 456 on database 1 from TSO but not from production CICS.
ABC's security requirements are satisfied, but XYZ can access file 456 from production CICS, even though it is not desired (because once a user has access to a resource, ADASAF will allow that access from any job which also has the necessary permissions).
To achieve this level of security, it is necessary to set the
XLEVEL
parameter to 3, which instructs ADASAF to verify a user's access to a resource
profile of the format:
uuuuuuuu.dddddddd.ffffffff
where:
| uuuuuuuu | is the User ID of the originating job |
| dddddddd.ffffffff | is the Database ID and file number, as in a standard ADASAF resource profile |
The resource profile length must be defined to the security system as 26 rather than 17. Therefore, the following definitions must be made in the security system:
| User | Class | Profile Name | Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC | ADASEC | PCICS.CMD00001.FIL00456 | Read, Update |
| XYZ | ADASEC | PCICS.CMD00001.FIL00456 | None |
| XYZ | ADASEC | XYZ.CMD00001.FIL00456 | Read |
And disallow access to undefined resources
(DBUNI=N) or define a profile name ABC.CMD00001.FIL00456
and give user ABC no access to it.
ADASAF now performs the following checks:
ABC accesses file 456 from production CICS
Does ABC have access to resource ADASEC /PCICS.CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
The access is allowed.
ABC accesses file 456 from TSO
Does ABC have access to resource ADASEC /ABC.CMD00001.FIL00456? No.
The access is rejected and the command receives response 200.
XYZ accesses file 456 from TSO
Does XYZ have access to resource ADASEC /XYZ.CMD00001.FIL00456? Yes.
The access is allowed.
XYZ accesses file 456 from production CICS
Does XYZ have access to resource ADASEC /PCICS.CMD00001.FIL00456? No.
The access is rejected and the command receives response 200.
The results of data access and update checks, both successful and unsuccessful, are cached by ADASAF. There are two levels of caching:
A generalized resource cache, which contains a given number of
user-based entries and holds the profile names for resources that have been
successfully checked for this SAF user. Both the number of entries and the
number of profile names per entry are configurable by parameter. This cache is
particularly effective in conjunction with the
LOGOFF=TIMEOUT/NEVER parameter as it precludes the need
to log on repetitively to the security system (and re-populate the cached
resources) in databases where users frequently log on to Adabas, do a small
amount of work and logoff again. Each user entry is (256 +
(DBNCU*17) + (NWNCU*17)) bytes in
size and, if there are more users than entries, the oldest entry is overwritten
when a new entry is required. The total size of this cache is specified by the
GWSIZE
parameter.
The second cache is a quick look-up cache and contains an entry for
each Adabas user (the number of entries is set to the value of the Adabas
NU parameter, plus 25%, so if NU
is 200, this cache will have 250 entries). Each entry contains 96 bytes of
fixed information and eight times the value of the
MAXFILES
parameter for holding information about files that the user has attempted to
access. Whenever a user accesses or updates an Adabas file, this cached file
list is checked to determine whether the user already has the necessary access
level.
You can use ADASAF to incorporate protection of Adabas Basic Services
into your SAF security repository. This option can be activated on a
nucleus-by-nucleus basis using the ABS
parameter. There are two levels of security, as follows:
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Only the main functions are protected. If a user has read
access to a main function, all subfunctions are automatically permitted
(ABS=1).
|
| 2 | Subfunctions are also protected. The user must have access to
the main function and the subfunction (ABS=2).
|
The resource check is performed against the resource class specified by
the DBCLASS parameter and the resource name is built in
accordance with the settings of the DBFLEN and
DELIM parameters. Access to undefined resources is
governed by the DBUNI parameter.
The following tables define the subfunctions for each Adabas Basic
Services function, together with the resource name that is checked (assuming
DBFLEN is set to 2 - 5 digits with leading zeros, and
DELIM=Y).
Before checking any of the individual resources, ADASAF establishes a user's right to use Adabas Basic Services against this nucleus by verifying that the user has read access to the resource ABSddddd.GENERAL.
Note:
The Subfunction Profile (listed in the following tables) is used only
when ABS=2 (subfunction protection).
| Function: | Session Monitoring |
|---|---|
| Function Profile: | ABSddddd.SESSION |
| Subfunction | Subfunction Profile* | Access |
|---|---|---|
| Display Cluster Members | ABSddddd.CLUSTER | Read |
| Display Installed Products | ABSddddd.DISINST | Read |
| Maintain User Profiles | ABSddddd.USER | Read |
| Display Parameters | ABSddddd.PARM | Read |
| Modify Parameters | ABSddddd.PARM | Update |
| Display Queues | ABSddddd.QUEUES | Read |
| Refresh Nucleus Statistics | ABSddddd.REFSTATS | Read |
| Current Resource Statistics | ABSddddd.STATS | Read |
| Maintain TCP/IP URL | ABSddddd.TCPIP | Read |
| Display Resource Utilization | ABSddddd.RESUTIL | Read |
| Display Maintenance Levels | ABSddddd.ZAPS | Read |
*Used only when ABS=2 (subfunction
protection)
| Function | Checkpoint Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Function Profile | ABSddddd.CHECKP |
| Subfunction | Subfunction Profile* | Access |
|---|---|---|
| List Checkpoints | ABSddddd.CHECKP | Read |
| Delete Checkpoints | ABSddddd.CHECKP | Update |
*Used only when ABS=2 (subfunction
protection)
| Function | File Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Function Profile | ABSddddd.FILE |
| Subfunction | Subfunction Profile* | Access |
|---|---|---|
| Define/Modify FDT | ABSddddd.FDT | Read |
| Release Descriptor | ABSddddd.REL | Read |
| Delete File | ABSddddd.DEL | Read |
| Define New File | ABSddddd.DEF | Read |
| Modify File Parameters | ABSddddd.MOD | Read |
| Reorder File Online | ABSddddd.ORD | Read |
| Refresh Rile to Empty | ABSddddd.REF | Read |
| Allocate/Deallocate File Space | ABSddddd.ALL | Read |
| Maintain Expanded Files | ABSddddd.EXP | Read |
*Used only when ABS=2 (subfunction
protection)
| Function | Database Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Function Profile | ABSddddd.DBMAINT |
| Subfunction | Subfunction Profile* | Access |
|---|---|---|
| Add New Dataset to Asso/Data | ABSddddd.ADD | Read |
| Increase/Decrease Asso/Data | ABSddddd.INCREASE | Read |
| List/Reset DIB Entries | ABSddddd.DIB | Read |
| Recover Unused Space | ABSddddd.RECOVER | Read |
| Uncouple Two Adabas Files | ABSddddd.UNCOUPLE | Read |
*Used only when ABS=2 (subfunction
protection)
| Function | Session Opercoms |
|---|---|
| Function Profile | ABSddddd.OPERCOMS |
| Subfunction | Subfunction Profile* | Access |
|---|---|---|
| Extended Error Recovery | ABSddddd.ERROR | Read |
| Force Dual Log Switch | ABSddddd.LOG | Read |
| Lock/Unlock Files | ABSddddd.LOK | Read |
| Reset Online Dump Status | ABSddddd.RDUMPST | Read |
| Stop User(s) | ABSddddd.STOPU | Read |
| Termination Commands | ABSddddd.TERM | Read |
| Manage Online Utilities | ABSddddd.UTILS | Read |
| Allocation/deallocation of CLOGs/PLOGs | ABSddddd.LOGALLOC | Read |
| User Table Maintenance | ABSddddd.USERTAB | Read |
*Used only when ABS=2 (subfunction
protection)
| Function | Database Report |
|---|---|
| Function Profile | ABSddddd.REPORT |
| Subfunction | Subfunction Profile* | Access |
|---|---|---|
| List Files with Critical Extents | ABSddddd.EXTENTS | Read |
| Display Field Description Table | ABSddddd.DFD | Read |
| Display File | ABSddddd.DIF | Read |
| General Database Layout | ABSddddd.LAYOUT | Read |
| List VOLSER Distribution | ABSddddd.VOLSER | Read |
| Display Asso/Data Block | ABSddddd.DRABN | Read |
| Display Unused Storage | ABSddddd.UNUSED | Read |
*Used only when ABS=2 (subfunction
protection)
| Function | Space Calculation Report |
|---|---|
| Function Profile | ABSddddd.SPACE |
The Space Calculation function has no subfunction profiles.
Assuming that an Adabas command satisfies the appropriate security
checks, ADASAF can automatically apply Adabas passwords and cipher codes if the
SAF security system is RACF. At nucleus initialization, ADASAF extracts the
INSTDATA field from the RACF profiles for all files in the current database (if
PRMDELIM=N, the ACC prefixed profiles are used) and
subsequently applies them to any command for the relevant file. Cipher codes
should be specified as
C=nnnnnnnn where
nnnnnnnn is the eight-digit cipher code. Passwords
should be specified as
P=xxxxxxxx, where
xxxxxxxx is the password. If a file has both, they
should be separated by a comma, for example
C=12345678,P=PASSWORD. A file may have only one cipher
code and one password.
The Adabas password and cipher code can be provided by a user exit
rather than being stored in RACF. This is activated by specifying
P=USEREXIT (or C=USEREXIT) in the
RACF INSTDATA field for the relevant file's profile. Then, whenever a command
passes security checks, ADASAF invokes the user exit and uses the returned
information as password or cipher code. Member ADASAFX1 in AAFvrs.SRCE contains
a sample user exit, a description of the interface, and instructions for
installing the exit.
As an alternative to using RACF INSTDATA, or for SAF security systems other than RACF, passwords and cipher codes may be provided at nucleus initialization time by user exit ADASAFX2. If ADASAFX2 is linked with SAFADA, no attempt is made to extract passwords and cipher codes from the security system. Instead, any passwords and cipher codes for files in the current database must be suplied by ADASAFX2.
See the section Password / Cipher Code Exits for more information.
Adabas operator commands entered from an MVS console can be secured by either controlling the predefined group to which the operator command belongs, or by grouping operator commands by keyword. A sample member, ADAEOPTB, is provided in the source library that defines operator commands as belonging to one of three groups, namely DISPLY, MODIFY, and SPECAL. The choice of keywords and how commands are grouped is decided on site, and determines which Adabas operator commands may be entered from an MVS console. If ADAEOPTB is not used, then the first eight characters of the command (up to a space or =) are used as the basis for validation.
Note:
Operator commands are allowed or disallowed based on either the User
ID of the user who starts the Adabas nucleus, or on the identifier of the
started task. The choice is not based on the User ID of the user
issuing the console command.
The following is a sample grouping as supplied in the ADAEOPTB source library member. The following list is not restricted to the commands shown here and can be added to or subtracted from, depending on installation requirements. For more information about Adabas operator commands, see the Adabas Operations documentation.
The display-type Adabas commands are:
CSTAT |
DHQ |
DONLSTAT |
DUQE |
CSUM |
DHQA |
DPARM |
DUUQE |
DAUQ |
DLOCKF |
DPPT |
DXCACHE |
DCQ |
DMEMTB |
DRES |
DXFILE |
DDIB |
DNC |
DSTAT |
DXLOCK
|
DDSF |
DNFV |
DTH
|
DXSTAT |
DFILES |
DNH |
DUQ |
|
DFILUSE |
DNU |
DUQA |
The modify-type Adabas commands are:
ADAEND |
CDATAEXT |
CFDISABLE |
FEOFPL |
CANCEL |
CDATAV64 |
CFENABLE |
FMXIO |
CASSODSP |
CDATAHSP |
CFILE |
HALT |
CASSOEXT |
CDATAMAX |
CFSTAT |
RDUMPST |
CASSOHSP |
CDELETE |
CINCLUDE |
RESUME |
CASSOMAX |
CDEMAND |
CLOGMRG |
REVIEW |
CASSOV64 |
CDISABLE |
CPARM |
TNAA |
CBUFNO |
CDISPSTAT |
CRETRY |
TNAE |
CCHANGE |
CENABLE |
CT |
TNAX |
CCTIMEOUT |
CEXCLUDE |
DUMP |
TT |
CDATADSP |
CFDELETE |
FEOFCL |
The special Adabas commands are:
ALOCKF |
LOGIB |
NOLOGRB |
SGMT |
AOSLOG |
LOGIO |
NOLOGSB |
STOPF |
ASYTVS |
LOGRB |
NOLOGUX |
STOPI |
CLUFREEUSER |
LOGSB |
NOLOGVB |
STOPU |
DELUF
|
LOGUX
|
ONLRESUME
|
SYNCC
|
DELUI
|
LOGVB
|
ONLSTOP
|
TCPIP
|
LOCKF
|
NOLOGCB
|
ONLSUSPEND
|
TM
|
LOCKU
|
NOLOGFB
|
RALOCKF
|
UNLOCKF
|
LOCKX
|
NOLOGGING
|
RALOCKFA
|
UNLOCKU
|
LOGCB
|
NOLOGIB
|
READONLY
|
UNLOCKX
|
LOGFB
|
NOLOGIO
|
REVIEWHUBID
|
UTIONLY
|
LOGGING
|
To validate authorization for operator commands, ADASAF checks for read access to an entity name of the format
| OPRdbid.type | if DELIM=Y
|
| OPRdbidtype | if DELIM=N
|
Where OPR is hard-coded, dbid specifies the
Database ID in the format appropriate to the setting of the
DBFLEN parameter; and type is
MODIFY, DISPLY or SPECAL if ADAEOPTB is used, or is the command name itself if
ADAEOPTB is not used.
For example, assuming that a standard ADAEOPTB is used, that
DELIM=Y and DBFLEN=2 (no leading
zeroes); when the operator issues a DSTAT command to
database 235, ADASAF will check that the User ID under which database 235 is
executing has read access to the resource OPR235.DISPLY.
Assuming that ADAEOPTB is not used, that DELIM=Y
and DBFLEN=2, when the operator issues a
STOPU=X'123' command to database 235, ADASAF will
check that the User ID under which database 235 is executing has read access to
the resource OPR235.STOPU.
Whether ADAEOPTB is used or not, ADASAF operator commands are always checked against type SPECAL.
With ADASAF and Entire Net-Work, remote Adabas calls to a multi-user node (MPM) can be validated when ADASAF is active on all participating MVS systems.
Entire Net-Work transports the User ID, which it obtains from the active
external system on the host node, to the target node. There, ADASAF uses the
User ID to construct the RACROUTE REQUEST=AUTH security
calls. Support for validation based on dynamic User ID strings or connect
groups is available.
The prerequisites for running ADASAF with Entire Net-Work are as follows:
All participating Entire Net-Work nodes that make remote calls to an Adabas nucleus with ADASAF active must be running a current version of Entire Net-Work. All Adabas components must be current;
An external security system like RACF, CA-Top Secret, and CA-ACF2 must be active on every Entire Net-Work /ADASAF MPM node. The external security systems can vary from node to node, since the external security information being transported by Entire Net-Work is in a format acceptable by all systems;
The Adabas SVC used by Entire Net-Work must be current and must be linked with the security extensions for ADASAF. See AAFvrs.JOBS(SAGI030) for the sample job stream that shows how to link ADASVC with SVCSAF.
When ADASAF is active on a multi-user (MPM) node, you can secure remote Adabas calls with Entire Net-Work for Workstations. The Adabas link routines supplied with Entire Net-Work provide the mechanism required for the two-phase logon described in the section Remote Workstation Logon. Once logon has been completed, all validation of resources occurs just as it does when the remote user is executing on the mainframe.
Additionally, as described in the section Alternatives to Remote Workstation Logon, ADASAF can secure remote Adabas calls by selecting the Entire Net-Work Node name of the remote caller, or the Entire Net-Work Link name used by the remote caller, as the user ID on which security checks are based. If you select either (or both - different databases can use different options) of these mechanisms, you must define the appropriate Node and Link names as users in your security system, with the correct access permissions for the relevant Adabas resources.
The external security User ID that is transported from the host node takes on the profile of the User ID in the external security system, the User ID must be defined with the proper authority to ensure access to only the proper Adabas resources.
A remote call to a target ADASVC with ADASAF active from an inactive external security node causes a security violation (response code 200) on the calling side.
MVS operator communication with ADASAF is achieved using the OS/390
Modify (F) command. All ADASAF operator commands are
prefixed with AAF. For example:
F ADA123,AAF SSTATADASAF provides an exit for encrypting and decrypting the user Logon ID and password during the two-phase remote logon process. The encryption/decryption algorithms that are used must produce the same result on the workstation as in the Adabas ADASAF mainframe user exit. Information is provided in the appropriate Entire Net-Work documentation.
If a user-provided exit is not used with ADASAF, ADASAF uses its own internal encryption/decryption routines during the logon. If a user exit is used, the user exit CSECT must be "ESIEXIT" and must be linked to the SAFADA module.
The following graphic illustrates the parameter list that ADASAF passes to the ADASAF user exit:

The following example shows how to link the ADASAF user exit ESIEXIT module into the ADASAF module:
//JOB //LKESI EXEC PGM=IEWL,PARM='XREF,LET,LIST,NCAL,REUS' //SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=* //SYSUT1 DD UNIT=SYSDA,SPACE=(CYL,(1,1)) //SYSLMOD DD DSN=YOUR.APF.LOADLIB,DISP=SHR (target execution loadlib) //AAFLIB DD DSN=AAFvrs.LOAD,DISP=SHR (distributed ADASAF loadlib) //YOURLIB DD DSN=YOUR.USER.EXIT.LOADLIB,DISP=SHR (user exit loadlib) //SYSLIN DD * INCLUDE AAFLIB (SAFADA) (ADASAF module) INCLUDE YOURLIB (ESIEXIT) (your encryption/decryption module) NAME SAFADA (R) /*
If you want ADASAF to provide Adabas passwords and cipher codes, but for any reason these cannot be stored in RACF (or you use a different security system), you may create a user exit to return the passwords and cipher codes to ADASAF.
The ADASAFX1 user exit is used to supply passwords/cipher codes at
Adabas command execution time. It is invoked for every file where the RACF
profile's INSTDATA specifies P=USEREXIT or
C=USEREXIT. The user exit must be re-entrant and must
have a CSECT name of ADASAFX1. Addressing mode on entry is 31-bit and the exit
must return in the same mode.
To link the exit into ADASAF, use a job similar to the following:
//LINKSAF EXEC PGM=IEWL, // PARM=`MAP,LET,LIST,XREF,NCAL,REUS' //SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=X //SYSUT1 DD UNIT=SYSDA,SPACE=(CYL,(1,1)) //AAFLOAD DD DSN=AAFvr1.LOAD,DISP=SHR //EXITLOAD DD DSN=your.LOAD,DISP=SHR //SYSLMOD DD DSN=your.LOAD,DISP=SHR must be APF-authorized //SYSLIN DD DDNAME=SYSIN //SYSIN DD * MODE AMODE(31),RMODE(24) SETCODE AC(1) INCLUDE AAFLOAD(SAFADA) INCLUDE EXITLOAD(ADASAFX1) NAME SAFADA(R)
The registers on entry to ADASAFX1 are as follows:
| R1 | Address of the parameter address list |
|---|---|
| RD | Address of two consecutive 18-word save areas |
| RE | Return address |
| RF | ADASAFX1 base address |
All registers must be restored to their contents on entry before returning to ADASAF.
R1 on entry contains the address of a six-word address list:
| Word 1 | Address of call type. Call type is a single byte. If set to X"80", ADASAF expects a password; if set to X"40", ADASAF expects a cipher code. |
|---|---|
| Word 2 | Address of return code. Return code is a full word. If set to X"00000000", ADASAF uses the value returned by the exit as password or cipher code. Otherwise, ADASAF leaves the Adabas control block unchanged. |
| Word 3 | Address of the database ID. The database ID is a two-byte binary number. |
| Word 4 | Address of the file number. The file number is a two-byte binary number. |
| Word 5 | Address of the returned password/cipher code. This is an eight-byte field containing binary zeros on entry. It should be set to the desired password or cipher code, which ADASAF inserts into the Adabas control block if the return code in parameter 2 is 0. |
| Word 6 | Address of the Adabas parameter list for the command being processed. The Adabas parameter list contains the addresses of the Adabas control block, format buffer, record buffer, search buffer, value buffer, and ISN buffer. |
The ADASAFX2 user exit is used to supply passwords/cipher codes at
nucleus initialization time. It is invoked by ADASAF during nucleus
initialization and may return a password and or a cipher code for as many files
as required (providing the value of MAXPC is not
exceeded). The user exit must be re-entrant and must have a CSECT name of
ADASAFX2. Addressing mode on entry is 31-bit and the exit must return in the
same mode.
To link the exit into ADASAF, use a job similar to the following:
//ADASAF EXEC PGM=IEWL, // PARM='MAP,LET,LIST,XREF,NCAL,REUS' //SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=X //SYSUT1 DD UNIT=SYSDA,SPACE=(CYL,(1,1)) //AAFLOAD DD DSN=AAFvrl.LOAD,DISP=SHR //EXITLOAD DD DSN=your.LOAD,DISP=SHR //SYSLMOD DD DSN=your.LOAD,DISP=SHR must be APF-authorized //SYSLIN DD DDNAME=SYSIN //SYSIN DD * MODE AMODE(31),RMODE(24) SETCODE AC(1) INCLUDE AAFLOAD(SAFADA) INCLUDE EXITLOAD(ADASAFX2) NAME SAFADA(R)
The registers on entry to ADASAFX2 are as follows:
| R1 | Address of the parameter address list |
|---|---|
| RD | Address of an 18-word save area |
| RE | Return address |
| RF | ADASAFX2 base address |
All registers must be restored to their contents on entry before returning to ADASAF.
R1 on entry contains the address of a five-word address list:
| Word 1 | Address of Database ID. The Database ID is a two-byte binary number. ADASAF passes the current Database ID to the exit. |
|---|---|
| Word 2 | Address of return code. The return code is a four-byte binary number and must be set by ADASAFX2. ADASAF will call the exit repetitively until the return code is not 0. If set to 0, ADASAF will use the values returned by the exit. If not 0, ADASAF will not call the exit again (but will still use the values returned on previous calls). |
| Word 3 | Address of file number. The file number is a two-byte binary number. The first time in, this will be X"0000". On subsequent calls it will contain the most recently returned file number. The exit must set it to the file number to which the returned password or cipher code applies. |
| Word 4 | Address of code type. This is a one-byte binary field. The exit must set this to X"40" when returning a cipher code and to X"80" when returning a password. |
| Word 5 | Address of an eight-byte password/cipher code. The exit must set this to the appropriate password or cipher code. If ADASAFX2 sets this to USEREXIT, ADASAF will subsequently invoke ADASAFX1 to provide a password or cipher code at Adabas command execution time. |