The hyperdescriptor exits (hyperexits) 1 through 31 (HEX01...HEX31) are required to define the algorithm for user-supplied descriptor values (see the Adabas Utilities documentation ). A hyperexit is called by ADACMP or the Adabas nucleus whenever a hyperdescriptor value is to be generated. ADACMP always uses the hyperdescriptor exit specified in its own ADARUN statement. When ADAINV specifies a hyperdescriptor exit, the exit used is the one specified in the Adabas nucleus' ADARUN statement.
Note:
Hyperexits must return the same AMODE value to the calling program
that was active when the hyperexit was called.
This document covers the following topics:
| Parameter | Address of the beginning of the . . . |
|---|---|
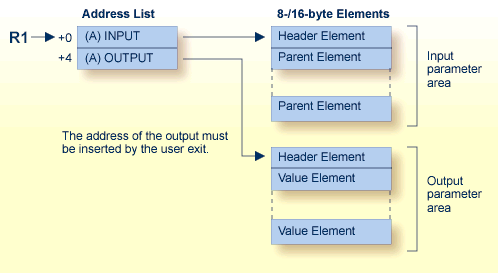
| 0 (R1) | input parameter area. |
| 4 (R1) | output parameter area. This address must be inserted by the user-written program. If no values are to be returned, the address value must be set to zero. |
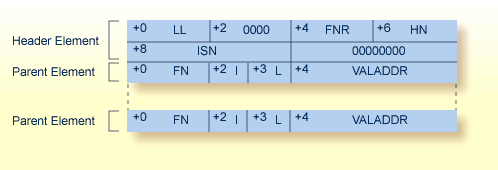
| LL | total length of the input parameter area, including this length field |
| FNR | file number |
| HN | name of the hyperdescriptor |
| ISN | ISN assigned to the record |
| FN | name of the parent field |
| I | periodic group index of the parent field. If the parent field is not part of a PE group, this byte contains a zero. |
| L | length of the value pointed to by VALADDR if the parent field is defined with the FI option. |
| VALADDR | address of the value of the parent field. The format of the value depends on the options of the fields. If the parent field is defined with the NU (null value suppression) option and the value for this field is suppressed, no input parameter element is created. |
The following examples show formats for the value pointed to by VALADDR for parent fields with combinations of the FI (fixed storage) and MU (multiple-value) options:
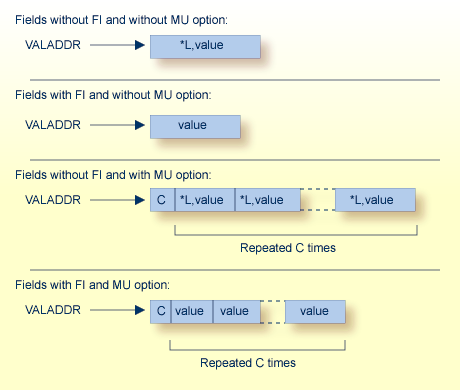
where
| C | is a one-byte value representing the MU count. |
| *L | is a hexadecimal value length, including this one- or two-byte length value. For lengths from 1 through 127, only a single byte is required. For lengths ranging 128 to 255, two bytes are needed: the first byte is set to X`80', and the second byte is set to the actual length value (see the following example table): |
| Length | Byte 1 | Byte 2 |
|---|---|---|
| L=127: | x`7F' | (x`80') |
| L=128: | x`80' | x`80' |
| L=255: | x`80' | x`FF' |
This area must be allocated and filled within the hyperdescriptor user exit. The address of this area must be placed into the 2nd position of the main parameter area.
This area consists of a 8-byte header followed by the generated hyperdescriptor values in compressed format.

| LL | total length of the output parameter area, including this length field. |
| 00 | reserved space. This must be set to zeros. |
| ISN | the ISN to be assigned to the descriptor values. If the original ISN is to be changed, the new ISN must be inserted here. If these four bytes contain zero on return to the Adabas nucleus, the original ISN is used. This is a four-byte binary value. |
Note:
If the hyperexit returns an ISN in the ISN field of the header
element, the file must be defined with USERISN=YES to prevent ISN reassignment
when the file is later reloaded.
| L | length of the following value, including this length byte. The maximum length depends on the format in use for the hyperdescriptor. |
| Value | the descriptor value to be inserted into the index. The value must follow the rules which are in effect for the format assigned to this hyperdescriptor. If the hyperdescriptor is defined with the PE option, one byte containing the one-byte PE index must immediately follow the value and be included in length L. The nucleus checks values of packed or numeric format for validity. Valid signs for packed fields are A,C,E,F (positive) and B,D (negative). The nucleus changes all signs to F or D. |
Examples:
| L | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 04 | R E D | |
| 06 | B L U E02 | where X'02' is a PE index |
| 03 | 123F | packed 123 |
| 04 | 123F01 | packed 123 in PE group with index 1 |
The NU (null value) option is possible for the hyperdescriptor and/or parent fields. The possible combinations are as follows:
The hyperdescriptor is not NU:
The parent field is not NU and the value is null, the hyperexit is called and the null value is passed.
The parent field is NU and the value is null, the hyperexit is called and no input parameter element is created for this parent field.
All parent fields are NU and all values are null, the hyperexit is called and no input parameter element is created for any parent field.
The hyperdescriptor is NU:
The parent field is not NU and the value is null, the hyperexit is called and the null value is passed.
The parent field is NU and its value is null, the hyperexit is called and no input parameter element is created for this parent field.
All parent fields are NU and all values are null, the hyperexit is not called.