This document describes the utility "ADARBA".
The following topics are covered:
The ADARBA utility is used to administrate the RBAC security definitions, which are stored in the RBAC system file in the database.
ADARBA creates and modifies basic security objects such as users and roles, and is used to grant or revoke permissions. See Authorization for Adabas Utilities for further information.
The database to be used must be online.
Note:
Each ADARBA command represents a transaction. This means that
modifications to the security definitions take effect immediately.
Important:
Access to this utility should be strictly limited to the
person or persons responsible for database security.
This utility is a multi-function utility.
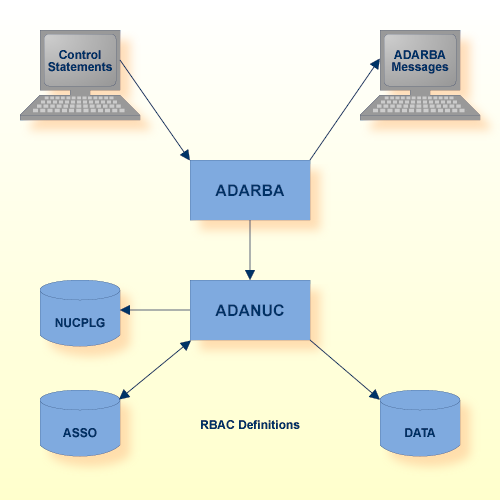
| Data Set | Logical Name | Storage Medium | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| RBAC Definitions | Database/RBAC System File | ||
| Control statements | stdin/SYS$INPUT | Utilities Manual | |
| ADARBA messages | stdout/SYS$OUTPUT | Messages and Codes |
The utility writes no checkpoints.
The following control parameters are available:
[NO]ABORT CREATE ,{OPERATION|USER|OBJECT|ROLE} = string M DBID = number DROP ,{OPERATION|USER|OBJECT|ROLE} = string [NO]ECHO GRANT ,ROLE = string [,TO] ,USER = string GRANT ,OPERATION = string [,OBJECT = string] [,TO] ,ROLE = string GRANT ,OPERATION = { ANY|DELETE|INSERT|READ|UPDATE} ,OBJECT = number [,TO] ,ROLE = string LIST ,{OPERATION|USER|OBJECT|ROLE} [= string] LIST ,ASSIGNMENT, {USER|PERMISSION} MAINTAIN REVOKE ,ROLE = string [,FROM] ,USER = string REVOKE ,OPERATION = string [,OBJECT = string] [,FROM] ,ROLE = string REVOKE ,OPERATION = { ANY|DELETE|INSERT|READ|UPDATE} ,OBJECT = number [,FROM] ,ROLE = string [NO]STAT
Notes:
[NO]ABORT
This function turns forced termination on or off.
If ABORT is specified, ADARBA terminates execution in case of an error and returns an error status.
If ADARBA is executed in interactive mode, the default is NOABORT.
If ADARBA is called with parameters, the default is ABORT.
Note:
[NO]ABORT can be specified in interactive mode or, if an input
script is used to provide the RBAC security definitions, in the input
script.
adarba: abort %ADARBA-I-INP, abort %ADARBA-I-PAR, forced termination enabled
For this ADARBA session, forced termination is enabled.
CREATE ,{OPERATION|USER|OBJECT|ROLE} = string
This function creates an RBAC definition of a given type and value.
The value assigned to items of type USER must be a valid logon credential; e.g. user identification. These values are platform-specific:
Linux: user_identification
Windows: domain\user_identification
See Authorization for Adabas Utilities for further information.
adarba: create,user=domain\userid
The user definition domain\userid for Windows is created.
DBID = number
This parameter selects the database to be used.
Note:
The nucleus must be running.
adarba: dbid=200
The database currently being used is database 200.
DROP ,{OPERATION|USER|OBJECT|ROLE} = string
This function deletes an RBAC definition with the given type and value. If this RBAC definition is referenced by a user or permission assignment, the corresponding assignment is revoked implicitly to avoid incomplete RBAC definitions.
adarba: drop,user=NEWUSER
The user definition NEWUSER is deleted.
[NO]ECHO
This function turns the echo of the command input on or off. The default is ECHO.
Note:
[NO]ECHO can be specified in interactive mode or, if an input
script is used to provide the RBAC security definitions, in the input
script.
adarba: echo %ADARBA-I-INP, echo %ADARBA-I-PAR, echo input enabled
For this ADARBA session, echo input is enabled.
GRANT ,ROLE = string [,TO] ,USER = string
This function grants a role to a user.
adarba: grant,role=NEWROLE,to,user=NEWUSER
The user NEWUSER is assigned the role NEWROLE.
GRANT ,OPERATION = string [,OBJECT = string] [,TO] ,ROLE = string
This function grants a role the permission to perform an operation on an object.
adarba: grant,operation=ada.uti.opr,to,role=ANYROLE
The role ANYROLE is assigned the permission to perform the operation ada.uti.opr on the default object (DBID.CURRENT).
GRANT ,OPERATION = { ANY|DELETE|INSERT|READ|UPDATE} ,OBJECT = number [,TO] ,ROLE = string
This function grants a role the permission to perform the corresponding Adabas commands on an Adabas file of the default database (DBID.CURRENT).
The predefined operations DELETE, INSERT, READ and UPDATE are used to group the Adabas direct commands according to their functionality. ANY is a short notation for DELETE, INSERT, READ and UPDATE .
OBJECT is interpreted as the Adabas file number if the value is a valid Adabas file number. Other values, in particular DBID.CURRENT, are accepted as object but not interpreted.
adarba: grant,operation=read,object=12,to,role=ANYROLE
The role ANYROLE is assigned the permission to perform the operation READ on file number 12 of the current database.
adarba: grant,operation=any,object=12,to,role=ANYROLE
The role ANYROLE is assigned the permission to perform the operations DELETE, INSERT, READ and UPDATE on file number 12 of the current database.
LIST ,{OPERATION|USER|OBJECT|ROLE} [= string]
This function displays the RBAC definition, if a string value is supplied and the specified definition exists.
This function displays all active RBAC definitions of the type specified if no value is supplied.
adarba: list,role=PUBLIC PUBLIC
The role PUBLIC is displayed.
adarba: list,role= PUBLIC
The role PUBLIC is displayed because it is the only active role definition.
LIST ,ASSIGNMENT ,{USER|PERMISSION}
This function displays, according to the type specified, all active user or permission assignments.
adarba: list,assignment,user PUBLIC,PUBLIC
All user assignments are displayed.
MAINTAIN
This function deactivates obsolete user assignments.
Note:MAINTAIN can be specified in interactive mode or, if an
input script is used to provide the RBAC security definitions, in the input
script.
adarba: maintain any_role,inactive_user
The obsolete user assignment ‘any_role,inactive_user' is now deactivated.
REVOKE ,ROLE = string [,FROM] ,USER = string
This function revokes a role, which was granted to the user.
adarba: revoke,role=NEWROLE,from,user=NEWUSER
The role NEWROLE is revoked from user NEWUSER.
REVOKE ,OPERATION = string [,OBJECT = string] [,FROM] ,ROLE = string
This function revokes a permission, which a role was granted, to execute an operation on an object.
adarba: revoke,operation=ada.uti.dbm,from,role=NEWROLE
The permission, which the role NEWROLE had been granted, to perform the operation ada.uti.dbm on the default object DBID.CURRENT, is revoked.
REVOKE ,OPERATION = { ANY|DELETE|INSERT|READ|UPDATE} ,OBJECT = number [,FROM] ,ROLE = string
This function revokes a permission, which a role was granted, to perform the corresponding Adabas commands on an Adabas file of the default database (DBID.CURRENT).
The predefined operations DELETE, INSERT, READ and UPDATE are used to group Adabas direct commands according to their functionality. ANY is a short notation for DELETE, INSERT, READ and UPDATE .
OBJECT is interpreted as the Adabas file number if the value is a valid Adabas file number.
adarba: revoke,operation=read,object=12,from,role=NEWROLE
The permission, which the role NEWROLE had been granted, to perform the operation READ on file number 12 of the current database, is revoked.
adarba: revoke,operation=any,object=12,from,role=NEWROLE
The permission, which the role NEWROLE had been granted, to perform the operations DELETE, INSERT , READ, and UPDATE on file number 12 of the current database, is revoked.
[NO]STAT
This function enables or disables the display of command statistics. The default is STAT.
Note:
[NO]STAT can be specified in interactive mode or, if an input
script is used to provide the RBAC security definitions, in the input
script.
adarba: stat %ADARBA-I-INP, stat %ADARBA-I-PAR, command statistics enabled
Command statistics are enabled for this ADARBA session.