This section contains information about Adabas TCP/IP (ADATCP) and how it can be used as an access method that provides point-to-point connections between the client application and the Adabas Server. It covers the following topics:
ADATCP is the new access method that provides point-to-point connections between the client application and the Adabas Server. It is covered by the Adabas Client Interface and the Adabas Server and it is intended for remote database access, although local access via ADATCP is also possible. The currently used access method based on IPC (local or remote via WCP) is still the default method for client applications. The TCP/IP access method can be chosen by using a configuration file on the client side and by configuring the Adabas server via new nucleus parameters. The usage of the new method is transparent for the client application.
The following picture gives an overview of typical setup:
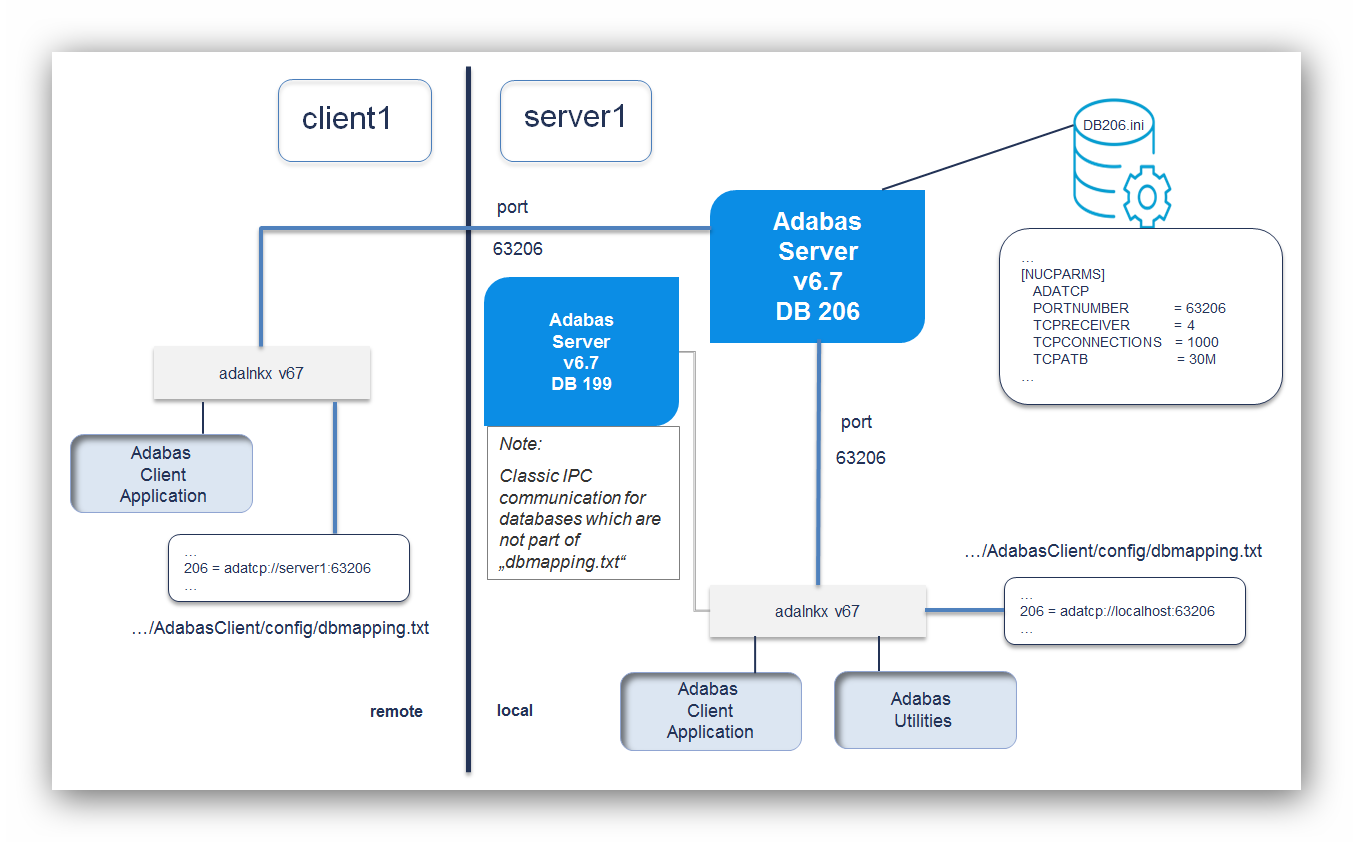
To enable ADATCP for an Adabas database, additional nucleus
parameter settings are required, like the ADATCP switch and
PORTNUMBER. Classic IPC communication is still possible.
To enable ADATCP for a client application, add a connection string for the database ID to the Adabas Client (ACL) configuration file (dbmapping.txt).
In the example above, database 206 is configured to use ADATCP and database 199 to use classic IPC communication.
With the release of Adabas Version 6.7, a new TCP/IP-based access method is provided. This new method supports the following scenarios:
Support Adabas running in a Docker container where TCP/IP is the standard communication method between containers.
Point-to-Point communication.
Easy configuration.
Reduced topology.
Therefore, the Adabas server as well as the Adabas client have been extended. The IPC based communication is still available.
The following table provides an overview of the new Adabas nucleus parameters available for ADATCP:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
[NO]ADATCP |
Enable the TCP/IP receiver (NOADATCP to disable it) |
PORTNUMBER
|
The TCP/IP port the database listens on. |
TCPRECEIVER |
Number of receiver threads. |
TCPCONNECTIONS |
Maximum number of parallel connections per receiver thread. |
TCPATB |
Attached buffer size for each TCP/IP receiver (similar to LAB/LABX). These buffers are exclusively used by the TCP/IP receiver and are not IPC based. |
The ADATCP option needs to be licensed. If this license (the Entire Net-Work license) is missing, ADATCP cannot be enabled. Please read section Licensing for a complete overview of licensing options.
To run the Community Edition of Adabas a license is not required, neither the Adabas license nor the Entire Net-Work license. However, the Community Edition restricts the ADATCP parameters to the following values:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
TCPRECEIVER |
1 |
TCPCONNECTIONS |
4 |
TCPATB |
10 MB |
Examples and default values can be found in the corresponding ADANUC documentation.
Note:
Please ensure that the database was started using the required ADATCP parameter settings. The following initialization message is written to the Adabas nucleus logfile during a successful startup:
ADANUC-I-ADATCPENAB, Adatcp enabled, listening on port: ...
Then you may continue to change the local Adabas Client configuration file.
To enable TCP/IP access for existing client applications without any change of the application, a configuration file needs to be updated with the according TCP/IP settings of the database. Please keep in mind that all Adabas utilities are also a kind of client application for the Adabas nucleus.
For each TCP/IP enabled database an entry needs to be added to the configuration file dbmapping.txt:
<dbid> = adatcp://<fqdn>:<port>
where fqdn means "fully qualified domain
name". Example for database 200 which runs on host
srvada01 and listens on port 61200:
200 = adatcp://srvada01.softwareag.com:61200
For UNIX/Linux the default path and file name of the configuration file is ${ACLDIR}/config/dbmapping.txt.
For Windows the default path and file name of the configuration file is %ACLDIR%\..\config\dbmapping.txt.
These entries describe the mapping of Adabas DBIDs to a connect
string with the appropriate TCP/IP parameters needed on the client side. If a
different mapping file should be used, the path name can be specified by the
environment variable ADA_DB_MAPPING.
Important:
The database definition in the configuration file decides
whether a database will be accessed via TCP or via IPC. If a database was added
to the mapping file, only TCP/IP communication will be used. No other
communication method (neither local IPC communication nor Entire Net-Work) is
used. See also Troubleshooting.
The point-to-point communication with Adabas on Linux, UNIX and Windows based on TCP/IP is part of the Entire Net-Work solution regardless whether the client using this communication method is local or remote to the database. It is still possible and recommended to use the IPC communication for local interaction with the database.
The following table provides an overview of the different licensing possibilities regarding ADATCP:
| License Available | ADATCP Activation |
|---|---|
| ADA + WCP | full |
| ADA | disabled |
| WCP | Community Edition with restrictions |
| None | Community Edition with restrictions |
Appropriate messages are provided in the nucleus log file.
 Activating the Entire Net-Work License on Linux/Unix
Activating the Entire Net-Work License on Linux/Unix
Copy the license key to a temporary location on your machine.
Change your directory to the Adabas/INSTALL directory of your main installation directory.
Execute the following adalic command to activate the license file:
adalic activate license_file
Where license_file is the fully qualified path to your license file.
 Activating the Entire Net-Work License on Windows
Activating the Entire Net-Work License on Windows
Copy the license key to a temporary location on your machine.
Start a Command Prompt to activate the license via the Start menu under: All Programs> Start Menu group name > Administration > Adabas 6.7 > Activate License.
In the Command Prompt execute the following adalic command to activate the license file:
adalic activate license_file
Where license_file is the fully qualified path to your license file.
New keywords are available or output has been changed for the following utility commands:
ADAOPR ... DISPLAY=TCPCONNECTIONS
ADAOPR ... TCPDISCONNECT=<ID>
ADAOPR ... DISPLAY=STATIC_PARAMETERS
The Adabas Client program getdbinfo has been extended
to print not only Adabas version and operating system information, but also an
Adabas subcode in case of problems as well as the established communication
type.
Output in case of problems:
adabas@server1> getdbinfo 199 get platform and version info of database 199 Database 199 .. ** Response code 148 (subcode=1034) from ADABAS for Open call adabas@server1> getdbinfo 206 get platform and version info of database 206 Database 206 .. ** Response code 148 (subcode=1038) from ADABAS for Open call, adatcp access to 'server1.aan.xy.sag:63206'
Output in case of success:
adabas@server1> getdbinfo 199 get platform and version info of database 199 Database 199 is active, V6.7.0.0, Platform = 20, opsys=UNIX/Windows, classic local access adabas@server1> getdbinfo 206 get platform and version info of database 206 Database 206 is active, V6.7.0.0, Platform = 20, opsys=UNIX/Windows, adatcp access to 'server1.aan.xy.sag:63206'
Interaction of NT and TCPRECEIVER parameter:
After analyzing our heavy load test results, we recommend to maximum increase/decrease the value for "number of receiver threads" (TCPRECEIVER) by a factor of 2 in comparison to the "number of threads be established for the Adabas session" (NT).
NT/2 <= TCPRECEIVER <= 2*NT
Q: Is it possible to get information about the client communication type without checking the configuration file?
A: Yes, the Adabas Client
program getdbinfo has been extended to provide such
information.
Q: Different applications on one node need to be able to access the same database by either TCP or IPC. How can this been achieved?
A: Set the required TCP
parameters like ADATCP and
PORTNUMBER in the DBINI file of
your database and start it. Use an Adabas Client environment for the first
application without changing the configuration file to use classic IPC
communication. Use an additional Adabas Client environment for the application
which should use TCP and add the necessary connection information in the
configuration file or use the ADA_DB_MAPPING
environment variable with a prepared configuration file before starting this
application.
Q: Customer has hundreds of clients and wants to migrate to TCP step by step. Do you have any recommendations?
A: To avoid copying a prepared
configuration file or adapt the existing dbmapping.txt
file in the Adabas Client (ACL) config folder, we
recommend to set the environment variable
ADA_DB_MAPPING and use a prepared configuration
file on a shared folder for all clients.
Q: After trying out ADATCP, how can I switch back to the classic IPC communication method?
A: Delete the database entry from the dbmapping.txt file. The database might still be ADATCP enabled, but all clients are using the classic IPC access method from now on.
ADATCP nucleus parameter values can neither be added nor updated while the database is up.
ADAOPR display=tcpconnections returns incomplete data on HP-UX and SUN.
Currently we do not provide any SSL support.