The configuration of security for utilities is stored in the following files:
adaauth.ini
adaaudit.ini
adarbac.ini
These files configure the security for a local machine and apply to all databases, to all product installations and product versions that are greater than or equal to Version 6.5 on the machine.
These are ASCII files, which can be edited with a standard text editor.
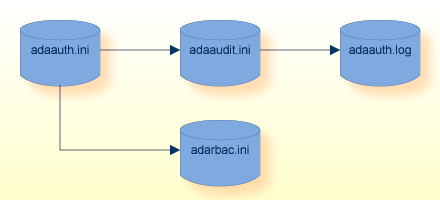
The configuration file adaauth.ini is located
centrally. The location is platform-specific and is fixed; e.g. cannot be
modified. Initially, the files adaaudit.ini and
adarbac.ini are also located in the predefined location. These
files can be moved as required to other locations.
| File | Description | Fixed Location |
|---|---|---|
adaauth.ini |
Configuration Definitions | Yes |
adarbac.ini |
Security Definitions | No |
adaaudit.ini |
Audit Log Configuration | No |
adaaudt.log |
Audit Log | No |
Note:
It is mandatory that all users, which are authorized to execute
an Adabas utility, have READ/WRITE access permissions to both the LOG_FILE and
the directory in which it is located.
The configuration and audit log files are installed into the following locations:
%PROGRAMDATA%\Software AG\Adabas\auth
adaauth.ini
adarbac.ini
adaaudit.ini
%PROGRAMDATA%\Software AG\Adabas\log
adaaudit.log
The configuration and audit log files are installed into the following locations:
/etc/softwareag/Adabas/auth
adaauth.ini
adarbac.ini
adaaudit.ini
/var/log/softwareag/Adabas
adaaudit.log
Important:
The configuration and audit log files mentioned above are
installed without restrictive file permissions. Please refer to
Security
Considerations in the section Adabas Security
Facilities of the Administration documentation,
for further details on how to secure (“harden”) the dataset.
All users of Adabas utilities require the following minimal file and directory permissions:
READ-privileges to the configuration files.
WRITE-privileges to the Audit Log File (LOG_FILE setting)
WRITE-privileges to the directory in which the Audit Log File is located.
The configuration file adaauth.ini contains information
which applies to the machine and to all databases, to all product installations
and product versions that are greater than or equal to Version 6.5 on the
machine.
This file contains the following basic security definitions:
The location of the security configuration definitions.
The location of the audit configuration file.
The configuration file adaauth.ini contains a single
section with the topic AUTHZ.
The section starts with a line containing the name of the topic
enclosed in square brackets, using the syntax
[topic-name]. The topics relevant to
security definitions are:
AUTHZ, with items
ACTION
AUDIT_FILE
MODE
RBAC_FILE
The topic AUTHZ contains information used to configure security for the local machine.
The syntax for the topic AUTHZ is as follows:
[AUTHZ] ACTION = <activation of feature> MODE = <source of definitions> AUDIT_FILE = <path to adaaudit.ini> RBAC_FILE = <path to adarbac.ini> [AUTHZ-END]
The item ACTION activates the authorization for Adabas utilities feature.
YES
enables the feature.
NO
disables the feature.
The default setting is NO.
Important:
The item ACTION will be depreciated in a future
release.
The item MODE defines the source of the security definitions.
ADABAS
The security definitions are defined in the RBAC system
file.
INI
The security definitions are defined in configuration
files.
The item AUDIT_FILE defines the location of the file
adaaudit.ini, which contains the configuration of the audit
processing; e.g. the layout and location of the audit log.
The item RBAC_FILE defines the location of the file
adarbac.ini, which contains the security definitions for the usage
of database utilities.
The configuration file adaaudit.ini contains
information which applies to the machine and to all databases, to all product
installations and product versions that are greater than or equal to Version
6.5 on the machine.
This file contains the following information:
Basic configuration audit file processing; e.g. the layout and location of the audit log.
The configuration file adaaudit.ini contains a single
section with the topic AUDIT.
The section starts with a line containing the name of the topic
enclosed in square brackets, using the syntax
[topic-name]. The topics relevant to
security definitions are:
AUDIT, with items
FORMAT
LOG_FILE
SEPARATOR
The topic AUDIT defines the parameters of the Audit Log.
The syntax for the topic AUDIT is as follows:
[AUDIT] FORMAT = <file layout> SEPARATOR = <token separator> LOG_FILE = <log file name> [AUDIT-END]
The item FORMAT defines the layout of an audit log entry.
TEXT
All values in the audit entry are preceded by a header and
separated by blanks.
CSV
All values in the audit entry are separated by the separator
value.
The item SEPARATOR defines the character to be used to separate values in CSV format.
Valid parameter values for SEPARATOR are:
| Parameter Value | Description |
|---|---|
"," |
Comma |
";" |
Semi-Colon |
"/t" |
Tabulator |
" "
|
Blank (Default) |
The parameter value must be quoted.
Note:
The parameter value for Tabulator is the string
"/t".
The item LOG_FILE defines the location and file name of the audit log.
The items in the log file entry depend upon value set in the item
FORMAT. They are thus either prefixed and separated by blanks
(FORMAT=TEXT) or are separated by the chosen separator value
without a prefix (FORMAT=CSV plus value selected in
SEPARATOR).
| Prefix | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
2016-06-02T14:48:19Z |
Timestamp | |
HOSTNAME= |
<hostname> |
Hostname of Machine |
OSVERSION= |
<operating_system> |
Name and Version of operating system |
%AUTHORIZATION-x |
Message indicator: (I)nformation or (E)rror | |
USER= |
Unix:
Windows:
|
Name of user account |
OPERATION= |
<operation> |
Name of attempted operation |
DBID= |
<number> |
Database ID |
AUTHORIZED= |
YES|NO |
Result of Authorization Request |
The configuration file adarbac.ini contains information
which applies to the machine and to all databases, to all product installations
and product versions that are greater than or equal to Version 6.5 on the
machine.
This file contains the security definitions for the usage of database utilities; e.g.:
User/Role assignments
Role/Permission assignments
Permissions, definitions of permitted operations on objects
Object definitions
Operation definitions
The configuration file adarbac.ini is divided into
sections, with one or more topics per section. Each section of the file starts
with a line containing the name of the topic enclosed in square brackets, using
the syntax [topic-name]. The relevant
topics are:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
USER_ROLE |
Definition of users and the assignment of roles. |
ROLE_PERMISSION |
Definition of roles and the assignment of permissions. |
PERMISSIONS |
Definition of permissions and the assignment of operations and an object, on which the operations may be performed. |
OBJECTS |
Definition of objects and the assignment of database IDs. |
OPERATIONS |
Definition of operations and the assignment of Adabas utilities. |
The topic USER_ROLE contains the assignment of roles to user accounts.
The syntax for the topic USER_ROLE is as follows:
[USER_ROLE] <user_name> = <role_assignments> [USER_ROLE-END]
The USER_ROLE topic may contain one or more USER_ROLE definitions, each of which assigns one or more roles to a user_name.
A USER_ROLE definition assigns one or more roles to a user_name and is an item in the USER_ROLE topic.
The syntax for a USER_ROLE definition item is as follows:
<user_name> = <role_name [,<role_name>] >
The value of the user_name can either be:
The name of the user (on Windows the domain\user) that is associated with the session and which has been validated by the operating system or
an asterisk (*) implying all users.
Note:
The values of user_name are case-insensitive, thus
uppercase and lowercase user_name values are considered to be
equal.
The value of the role_name can be any of the
following:
The name of a ROLE_PERMISSION definition.
A comma separated list of ROLE_PERMISSION definitions.
The topic ROLE_PERMISSION contains the assignment of permissions to roles.
The syntax for the topic ROLE_PERMISSION is as follows:
[ROLE_PERMISSION] <role_name> = <permission_assignments> [ROLE_PERMISSION-END]
The ROLE_PERMISSION topic may contain one or more ROLE_PERMISSION definitions, each of which assigns one or more PERMISSION definitions to a role_name.
A ROLE_PERMISSION definition assigns one or more roles to a role_name and is an item in the ROLE_PERMISSION topic.
The syntax for a ROLE_PERMISSION definition item is as follows:
<role_name> = <permission_name [,permission_name] >
The value of the permission_name can either be:
The name of a PERMISSIONS definition,
A comma separated list of PERMISSIONS definitions.
The topic PERMISSIONS contains the assignment of objects and operations to permissions. Each entry defines a tuple of permitted operations, which may be performed on a specific set of objects.
The syntax for the topic PERMISSIONS is as follows:
[PERMISSIONS] [<permission_definition>] [PERMISSIONS-END]
The PERMISSIONS topic may contain one or more PERMISSION definitions.
Each PERMISSION definition is a sub-topic to the PERMISSIONS topic and is identified by a unique name and contains an OBJECT and an OPERATION item, which are defined in the appropriate sections of the file.
The name of the PERMISSION definition must be unique and must be enclosed in brackets, as it is a sub-topic.
The syntax for the topic PERMISSION definition sub-topic is as follows:
[<permission_name>] OPERATION = <operation_name> OBJECT = <object_name> [<permission_name>-END]
Each PERMISSION definition must contain one OPERATION item and one OBJECT item:
The value of an OPERATION item is the name of an OPERATION definition, which defines the operations that may be performed.
The value of an OBJECT item is the name of an OBJECT definition, on which the operations may be performed.
The topic OBJECTS contains one or more OBJECT definitions. Each entry may be used in one or more PERMISSION definitions and assigns one or more database IDs to an object_name.
The syntax for the topic OBJECTS is as follows:
[OBJECTS] <object_definitions> [OBJECTS-END]
Each OBJECT definition is a sub-topic to the OBJECTS topic and is identified by a unique name and contains a DBID item.
The name of the OBJECT definition must be unique and must be enclosed in brackets, as it is a sub-topic.
The syntax for the topic OBJECT definition sub-topic is as follows:
[<object_name>] DBID = <number> [, <number>] [, <number>-<number>] [<object_name>-END]
Each OBJECT definition must contain a DBID entry which can be:
A single database ID,
A comma separated list of database IDs,
A range of database IDs separated by hyphen-symbol (‘-‘),
A combination of a list and a range of database IDs, or
An asterisk (*) implying all database IDs.
The topic OPERATIONS contains one or more OPERATIONS definitions. Each entry may be used in one or more PERMISSION definitions and assigns one or more utility operations to an operation_name.
The syntax for the topic OPERATIONS is as follows:
[OPERATIONS] <operation_definitions> [OPERATIONS-END]
The OPERATIONS topic may contain one or more OPERATION definitions.
An OPERATION definition is an item and assigns one or more utility operations to a unique name. Each OPERATION definition is used as value in a PERMISSION definition.
The name of the OBJECT definition must be unique and must be enclosed in brackets, as it is a sub-topic.
The syntax for the topic OPERATION definition is as follows:
<operation_name> = <utility_name [, <utility_name>]>
The value of the operation_name can be any of the following:
The name of an Adabas utility,
A comma separated list of names of Adabas utilities.
Below is a list of valid Adabas utility names:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
ada.uti.bck |
Backup and restore database or files |
ada.uti.dbm |
Database modification |
ada.uti.ela |
Configure Adabas Analytics |
ada.uti.fdu |
File definition |
ada.uti.frm |
Format and create a new database |
ada.uti.opr |
Operator utility |
ada.uti.ord |
Reorder the database or export / import files |
ada.uti.rba |
Administration of RBAC definitions |
ada.uti.rec |
Recovery of database or files |
ada.uti.rep |
Database report |
ada.uti.scr |
Manages and enables security functionality |
ada.uti.uld |
File unloading |
Note:
The values of utility_name are
case-sensitive. Invalid entries will result in a processing error; e.g. invalid
permissions.
The following limitations and/or restrictions apply to entries in
the adarbac.ini file.
| Description | Limitation / Restriction |
|---|---|
| Line | Must not exceed a maximum of 2064 characters. |
| Value | Must not exceed a maximum of 2036 characters. |
| Name of a USER | Must not exceed a maximum of 128 characters. |
| Name of a ROLE | Must not exceed a maximum of 32 characters. |
| Name of a PERMISSION | Must not exceed a maximum of 19 characters. |
| Name of an OPERATION | Must not exceed a maximum of 128 characters. |
| Name of an OBJECT | Must not exceed a maximum of 19 characters. |
| File Path | Must not exceed a maximum 255 characters. |
| File Name | Must not exceed a maximum 32 characters. |
| Value, Embedded Whitespace | Value must be enclosed with the quote character (‘”’). |
| Value, List of Values | Multiple values are separated commas (‘,’). |
| Value, Range of Values | The asterisk character ‘*’ indicates a range of all valid values. The usage is restricted to USER_ROLE and DBID entries. |
| Line, Continuation Character | Not available; entries are limited to the contents of a line. |
| Comment Line | Comments start with the hash symbol (‘#’). |
| Line-Comment | The comment begins with the first whitespace. |
| Duplicate Entries | Previous entry values are overwritten by the duplicate entry. The last entry value is used. |
The security definitions provided below implement an unrestricted access:
###
### SAMPLE: Access Permissions (Unrestricted Access)
###
### Users: Generic Definition
###
### Roles: DBADMIN Administrator (Database)
### FILEADMIN Administrator (File)
### DBREPORT Reporting (Database)
### USER User (Database)
###
### Role Assignment:
### All users are assigned all roles
### which provides the user with the permissions
### to execute operations as was in previous product releases
###
###
### Generic definition of Users and the Assignment of Roles
[USER_ROLE]
* = DBADMIN,FILEADMIN,REPORTER,USER
[USER_ROLE-END]
### Assignment of Permissions to Roles
[ROLE_PERMISSION]
DBADMIN = DBADMIN_PERM
FILEADMIN = FILEADMIN_PERM
REPORTER = REPORTER_PERM
USER = USER_PERM
[ROLE_PERMISSION-END]
### Definition of Permissions - Tuples of Operations on Objects
[PERMISSIONS]
[DBADMIN_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = ALL_OPERATIONS
[DBADMIN_PERM-END]
[FILEADMIN_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = FILE_OPERATIONS
[FILEADMIN_PERM-END]
[REPORTER_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = REPORT_OPERATIONS
[REPORTER_PERM-END]
[USER_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = USER_OPERATIONS
[USER_PERM-END]
[PERMISSIONS-END]
### Definition of Objects
[OBJECTS]
[OBJECT_ANY]
DBID = *
[OBJECT_ANY-END]
[OBJECTS-END]
### Definition of Operations
[OPERATIONS]
ALL_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.bck,ada.uti.dbm,ada.uti.ela,ada.uti.fdu,ada.uti.opr,ada.uti.ord,ada.uti.rba,ada.uti.rec,ada.uti.rep,ada.uti.scr,ada.uti.uld
FILE_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.fdu,ada.uti.ord,ada.uti.uld
REPORT_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.rep
USER_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.none
[OPERATIONS-END]
### EOF
The security definitions provided below implement the Least Amount of Privileges:
###
### SAMPLE: RBAC Security (LEAST AMOUNT OF PRIVILEGES)
###
### Users: Explicitly Defined
###
### Roles: DBADMIN Administrator (Database)
### FILEADMIN Administrator (File)
### DBREPORT Reporting (Database)
### USER User (Database)
###
### Role Assignment:
### Each user is explicitly defined and is assigned the minimum of roles and privileges.
### This enables the implementation of a "Least amount of Privileges" RBAC Security model.
###
### Explicit definition of Users and the Assignment of Roles
[USER_ROLE]
USRDBADMIN = DBADMIN
USRFILEADMIN = FILEADMIN
USRDBREPORT = DBREPORT
USR0001 = USER
[USER_ROLE-END]
### Assignment of Permissions to Roles
[ROLE_PERMISSION]
DBADMIN = DBADMIN_PERM
FILEADMIN = FILEADMIN_PERM
REPORTER = REPORTER_PERM
USER = USER_PERM
[ROLE_PERMISSION-END]
### Definition of Permissions - Tuples of Operations on Objects
[PERMISSIONS]
[DBADMIN_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = ALL_OPERATIONS
[DBADMIN_PERM-END]
[FILEADMIN_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = FILE_OPERATIONS
[FILEADMIN_PERM-END]
[DBREPORT_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = REPORT_OPERATIONS
[DBREPORT_PERM-END]
[USER_PERM]
OBJECT = OBJECT_ANY
OPERATION = USER_OPERATIONS
[USER_PERM-END]
[PERMISSIONS-END]
### Definition of Objects
[OBJECTS]
[OBJECT_ANY]
DBID = *
[OBJECT_ANY-END]
[OBJECTS-END]
### Definition of Operations
[OPERATIONS]
ALL_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.bck,ada.uti.dbm,ada.uti.ela,ada.uti.fdu,ada.uti.opr,ada.uti.ord,ada.uti.rba,ada.uti.rec,ada.uti.rep,ada.uti.scr,ada.uti.uld
FILE_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.fdu,ada.uti.ord,ada.uti.uld
REPORT_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.rep
USER_OPERATIONS = ada.uti.none
[OPERATIONS-END]
### EOF