This document covers the following topics:
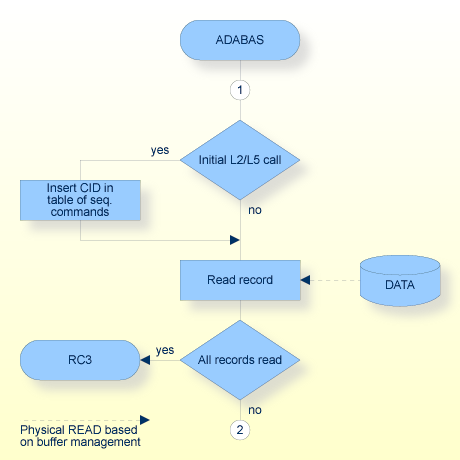
The L2 command is used to read a record from a set of records which are stored in physical sequence in Data Storage. Using the Multifetch feature, it is also possible to read multiple records with a single L2/L5 command.
The L2 command does not result in the reading of records in any particular logical order (unless the records were initially loaded in a particular logical sequence and no updating of the file which resulted in a change to this order has been performed).
Using the L2 command repeatedly, an entire file can be read at optimum speed since no access is required to the Associator (as with the L3 command), and all physical blocks are read in consecutive sequence.
The user specifies the file to be read and the fields within each record for which values are to be returned. The fields are specified in the format buffer. Adabas returns the requested field values in the record buffer.
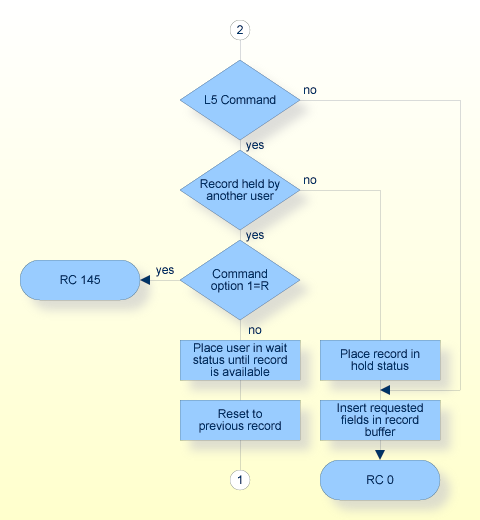
The L5 command performs the same function as the L2 command, and, in addition, places the record in shared or exclusive hold status, i.e. locks the record for other users. The L5 command should be used if the user needs to prevent other users from updating the record, e.g. because he wants to update the record. Please refer to Concepts and Facilities, Competitive Updating, Shared Locks and Hierarchical Locking for further information. If the user already holds a shared lock for the record, and requests an exclusive lock now, the lock is upgraded to the exclusive locking mode. If the user already holds an exclusive lock for the record, the locking mode remains unchanged.
If the previous command for this command ID was issued with the ‘Q’ option and the record read has not yet been released from shared hold status afterwards, this record read will be released from shared hold status again with the following exceptions:
If the same record has been read with the command option ‘Q’ in more than one command sequence, the record is only released if the next record has been read for all these command sequences, or an RC has been performed.
It is not released if another command has locked the same record exclusively, or the record has been shared locked with the command option ‘S’.
The L2/L5 command supports the Multifetch feature. This is indicated by one of the values `M' or `O' in the Command Option 1 field (see the description of the Command option 1 field for more details).
When the Multifetch feature is used, the maximum number of records which can be returned for a single L2/L5 call is limited by the following factors:
The ISN Lower Limit field can be used to specify the maximum number of records to be returned, thus avoiding internal overheads when only a limited number of records are required.
If the value in the ISN Lower Limit field is 0, the number of records returned is limited only by the size of the ISN/Multifetch Buffer and the Record Buffer.
| Field | Format | |
|---|---|---|
| Call Type | B | F/U |
| Reserved (internal use) | -/- | |
| Command Code | A | F/U |
| Command ID | B | F/U |
| File Number | B | F/U (1) |
| Response Code | B | F/A (1) |
| ISN | B | F/A |
| ISN Lower Limit | B | F/U |
| Format Buffer Length (ACB only) | B | F/U |
| Record Buffer Length (ACB only) | B | F/U |
| ISN Buffer Length (ACB only) | B | F/U |
| Command Option 1 | A | F/U |
| Command Option 3 (ACBX only) | A | F/U |
| Additions 2 | A,B | -/A |
| Additions 3 | A | F/A |
| Additions 5 | A | F/U |
| Command Time | B | -/A |
| User Area | F/U |
| Buffer | |
|---|---|
| Format Buffer | F/U |
| Record Buffer | –/A |
| Search Buffer | –/– |
| Value Buffer | –/– |
| ISN Buffer | –/A |
- Formats:
A alphanumeric B binary - x/y before/after Adabas call - x and y can take the values:
A Filled in by Adabas F To be filled in by User U Unchanged after Adabas call - Not used (1) The meaning of this field depends on the value specified for "Call Type". See Calling Adabas, The Control Block for details.
- Command Code
L2/L5
- Command ID
This field must be set to a non-blank, non-zero value. It is used by Adabas to provide the records in the correct physical order and to avoid the repetitive interpretation of the format buffer. The value provided must not be modified during any given sequential pass of a file.
The high-order byte of this field must not be set to hexadecimal `FF', except when automatic command ID generation is used (see Programming Considerations, Using Command IDs for additional information).
- File Number
The number of the file to be read.
- Response Code
Adabas returns the response code for the command in this field. Response code 0 indicates that the command was executed successfully.
Response code 3 indicates an end-of-file condition has been detected. Response codes 17, 18, 21, 23, 145 are possible as well.
If the Multifetch feature is used and an error occurs before or while processing the first record, the response code is returned in this field. In this case, the contents of the ISN Buffer and Record Buffer are undefined.
If an error is detected for the second or any subsequent ISN during the processing loop of the Multifetch feature, the first non-zero response code will terminate the multifetch processing. In this case, the response code will be stored as an additional entry in the ISN Buffer itself, not in the Response Code field of the Control Block. Since there are two possible locations for a response code, an application program should check first the Response Code field in the Control Block for errors of a general nature, then in the response code field of each ISN Buffer entry individually.
- ISN
If this field is set to zero before the initial L2/L5 call, the sequential pass will begin with the first record contained in the first physical block of the file.
If this field is set to an ISN value before the initial L2/L5 call, the sequential pass will begin at the first record physically located after the record identified by the ISN specified. The ISN specified must be present in the file, otherwise response code 23 will be returned.
This field need not be modified by the user after the initial L2/L5 call.
Adabas returns the ISN of the record which has been read in this field.
If the Multifetch feature is used, the ISN returned in the control block is the ISN of the first record read.
- ISN Lower Limit
If the Multifetch feature is used, this field is used to limit the number of records to be returned. If this field is set to zero, the maximum number of records returned depends on the size of the record buffer and/or the size of the ISN buffer.
- Format Buffer Length (ACB only)
The format buffer length (in bytes). The format buffer area defined in the user program must be as large as (or larger than) the length specified.
- Record Buffer Length (ACB only)
The record buffer length (in bytes). The record buffer area defined in the user program must be as large as (or larger than) the length specified.
- ISN Buffer Length (ACB only)
The ISN buffer length (in bytes). If the length of the ISN buffer is less than 20 bytes, the Multifetch option will be ignored.
This field is only used in conjunction with the Multifetch feature.
- Command Option 1
An `R' in this field indicates that the return option is to be used. If an L5 command is issued, and the record to be read and held is currently held by another user, Adabas will return response code 145 rather than placing the user in wait status until the record becomes available.
An `M' in this field invokes the Multifetch feature. See Programming Considerations, Using The Multifetch Feature for additional information.
If the Multifetch feature is required with the Return option, the value `O' should be used instead of `M'.
- Command Option 3 (ACBX only)
The command option 3 is relevant only for an L5 command.
A ‘C’ in this field indicates that a shared lock is to be acquired for this record only as long as the command is active. If the record was already locked before, the record remains locked. Using this option avoids dirty reads: you see only the committed states of the record.
An ‘S’ in this field indicates that the record is to be placed in shared hold status. The lock will be released again when the current transaction is committed or backed out. If the command belongs to a subtransaction, the lock is also released when the current subtransaction is backed out. You can also release the lock with an RI command.
A ‘Q’ in this field indicates that the record is to be placed in shared hold status. The lock is released again at start of next sequential read command for this read sequence, or when one of the events happens that releases a record read with ‘S’ option, whichever happens first. If the same record is read by more than one command with ‘Q’ option, the record is released only when, for all these command sequences, either the next record has been read, or an RC command has been issued. If the same record has also been read by another command with ‘S’ option, or the record has been locked exclusively, the record is not released by reading the next record of the command sequence. The ‘Q’ option is not allowed in combination with the command option 1 = ‘M’ (multifetch feature).
A blank in this field indicates that the record is locked exclusively.
- Additions 2
If the command completes successfully,and at least one Adabas field is requested in the format buffer, Adabas returns in the first two bytes in this field the compressed record length of the data storage record that was accessed, in binary format. The last two bytes contain the length of the decompressed fields selected by the Format Buffer in binary format. If the Multifetch feature is used, this information refers to the first record read.
For some response codes, Adabas returns detailed information in this field. See Adabas Messages And Codes for further information.
- Additions 3
This field is used to provide a security password.
If the file to be used is not security protected, this field should be set to blanks. If the file is security protected, the user must provide a valid password.
Adabas sets this field to blanks during command processing to protect the integrity of any password provided.
- Additions 5
This field may be used to provide a separate format buffer ID that is used to identify the internal format buffer used for this command, or to provide a global format buffer ID.
As long as the first byte of the Additions 5 field is not alphanumeric, the value provided in the command ID field will also be used as the format buffer ID.
If the first byte is a lower case character, the bytes 5 to 8 of the Additions 5 field will be used as the separate local format buffer ID.
If the first byte is a digit or an upper case character, the Additions 5 field (8 bytes) will be used as a separate global format buffer ID, which means that the format buffer ID can be used by several users in parallel.
See Programming Considerations, Using Command IDs for additional information and examples.
The fields for which values are to be returned are specified in this buffer. Format buffer definition, syntax and examples are provided in Calling Adabas, Format and Record Buffers.
The format buffer may not be modified after the initial L2/L5 call has been issued.
Adabas returns the requested field values in this buffer. All field values are returned according to the standard length and format of each field, unless the user has explicitly requested a different length and/or format in the format buffer.
When the Multifetch feature is used, the Record Buffer can contain data returned from multiple records. The Record Buffer consists of several entries, whereby each entry contains the requested field values from a single record. The number of entries returned, and the length of each entry is stored in a corresponding entry in the ISN Buffer.
When the Multifetch feature is used with the ACB interface, the ISN Buffer contains information which describes the entries returned in the Record Buffer. If you use the Multifetch feature with the ACBX interface, multifetch buffers are used instead.
The first 4 bytes of the respective buffer specify the number of 16-byte entries which follow in the that buffer. Each 16-byte entry corresponds to an entry returned in the Record Buffer, and contains the following unsigned integer values (each 4 bytes long):
the length of the entry in the Record Buffer
the response code for the entry in the Record Buffer (this can be
different from the value in the Response Code field in the Control Block)
If
this value is non-zero, this means that an error occurred which caused the
multifetch processing to be terminated. In this case, there is no corresponding
entry in the Record Buffer.
the ISN
an unused field
The following additional considerations are applicable for the L2/L5 command:
The Command ID used with the L2/L5 command is internally saved and used by Adabas. It will be released by Adabas when an end-of-file condition is detected, when an RC or CL command is issued, or when the Adabas session is terminated. The same command ID must not be used by the user for another read sequential command until it has been released.
Command IDs are not released at the end of a global transaction (see the Administration Manual for additional information).
The user is permitted to update and/or delete records which he has read with an L2/L5 command. Adabas maintains information as to the next record to be provided to the user and is able to provide the correct next record despite any interim record update or or delete performed by this user. But it may be that he receives the same record more than once during a given sequential pass of the file.
If another user is updating the file being read with an L2/L5 command, or if the user performing the L2/L5 commands is updating or deleting a record in the file that is not the record currently read with the L2/L5 command, it is possible that the user reading with the L2/L5 command will not receive one or more records in the file, or that he receives one record more than once.
File 2 is to be read in physical sequential order. All the values for all the fields within each record are to be returned.
Command Code L2
Command ID EXL2 (non blank CID required)
File Number 2
ISN 0 (all records are to be read)
Format Buffer Length 3 (or larger)
Record Buffer Length 49 (or larger)
Command Option 1 b (Return option not used)
Additions 3 Password (file 2 is security protected)
Format Buffer RG.
The L2 call is repeated to obtain each successive record. The ISN field need not be modified between calls.
File 2 is to be read in physical sequential order. The values for fields RA, XA, and XB (3 bytes unpacked) are to be returned. Each record read is to be placed in hold status for updating purposes.
Command Code L5
Command ID EXL5 (non blank CID is required)
File Number 2
ISN 0 (all records are to be read)
Format Buffer Length 13 (or larger)
Record Buffer Length 21 (or larger)
Command Option 1 b (Return option not used)
Additions 3 Password (file 2 is security protected)
Format Buffer RA,XA,XB,3,U.
The L5 call is repeated to obtain each successive record. The ISN field need not be modified between L5 calls.
Each record held should be released by an ET command (ET logic users) or RI command (non-ET logic users).