This document covers the following topics:
The ET command is used for two purposes:
End of a logical transaction (command option ‘S’ has not been specified).
End of a subtransaction (command option ‘S’ has been specified).
An ET command without the command option ‘S’results in:
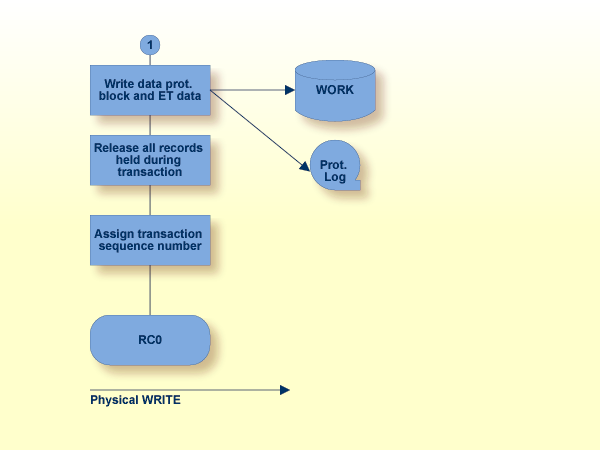
The writing of all current data protection information to the Adabas data protection log and Adabas work file for all update commands successfully executed during the transaction. This information may be needed by Adabas to apply all the updates which were performed during the transaction at the start of the next Adabas session. This will occur only if the current session is abnormally terminated (system failure) before these updates have been physically applied to the Associator and Data Storage;
Downgrade of all exclusive locks of the user to shared locks, if command option ‘H’ is used. Otherwise the release of all records held by the user (without multifetch option), or the release of all records specified in the ISN buffer (with the multifetch option);
Optionally, the storing of user data in an Adabas system file. This user data may be read subsequently with an OP or RE command and may be used for program restart;
The returning of a unique sequence number for the transaction by Adabas. This sequence number may be used to identify the last successfully processed transaction if a restart is necessary;
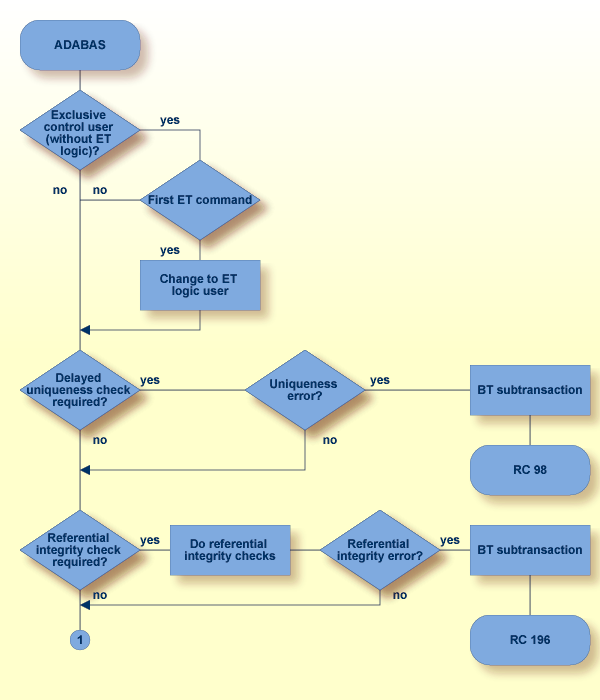
If subtransactions are activated, the end of the last subtransaction for the current transaction; this means if uniqueness and referential integrity checks have been delayed, they are performed now;
In the case of a uniqueness error, the current subtransaction is backed out, and a response code 98 is returned. In the case of a referential integrity error, the current subtransaction is backed out, and a response code 196 is returned. If you activated subtransactions but didn’t use subtransactions, i.e. you did not use an ET command with command option ‘S’, this means that the complete transaction is rolled back;
Note:
A referential integrity check can imply a large number of database
operations, e.g. if you specified cascaded delete in the referential integrity
constraint.
If subtransactions are activated, the start of the first subtransaction for the next transaction. A new savepoint is defined with savepoint ID 0.
The successful execution of an end of a logical transaction guarantees that all of the updates performed during the transaction will be applied to the database, regardless of any subsequent user or Adabas session interruption.
An ET command with the command option ‘S’results in:
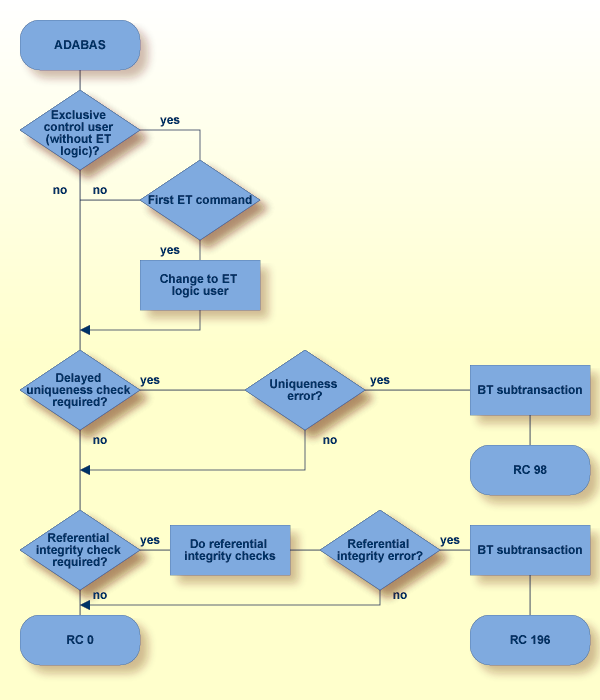
If subtransactions are not enabled for the current Adabas user session, response code 22 is returned; the first 2 bytes of the Additions 2 field are set to 19;
If there are uniqueness checks which have been delayed, they are performed now. In the case of a uniqueness error, the current subtransaction is backed out, and a response code 98 is returned. In the case of a referential integrity error, the current subtransaction is backed out, and a response code 196 is returned;
Note:
A referential integrity check can imply a large number of database
operations, e.g. if you specified cascaded delete in the referential integrity
constraint.
Start of the next subtransaction. A new savepoint ID is defined; the savepoint ID is returned in the command ID field of the control block. The new savepoint ID may be the same as the previous savepoint ID, if there were no lock or update activities after the previous savepoint.
Note:
Usually the savepoint ID is incremented by 1. For some
undocumented internal commands internal subtransactions are created. Therefore,
usage of these commands can result in larger savepoint IDs.
Note:
While the end of a logical transaction implies a commit, i.e. it is
guaranteed that all of the updates performed during the transaction will be
applied to the database, regardless of any subsequent user or Adabas session
interruption, there is no commit at the end of a subtransaction: With a backout
subtransaction you can backout all subtransactions belonging to a logical
transaction until the complete transaction is committed.
| Field | Format | |
|---|---|---|
| Call Type | B | F/U |
| Reserved (internal use) | -/- | |
| Command Code | A | F/U |
| Command ID | B | -/A |
| File Number | B | F/U (1) |
| Response Code | B | F/A (1) |
| Record Buffer Length (ACB only) | B | $ F/U |
| ISN Buffer Length (ACB only) | B | F/U (1) |
| Command Option 1 | A | F/U |
| Command Option 2 | A | F/U |
| Command Option 3 (ACBX only) | A | F/U |
| Additions 2 | A,B | -/A |
| Command Time | B | -/A |
| User Area | F/U |
| Buffer | |
|---|---|
| Format Buffer | $ */- |
| Record Buffer | $ F/U |
| Search Buffer | */– (2) |
| Value Buffer | */– (2) |
| ISN Buffer | F/U (2) |
| A | alphanumeric |
| B | binary |
| A | Filled in by Adabas |
| F | To be filled in by User |
| U | Unchanged after Adabas call |
| - | Not used |
| * | Not used but must be included in parameter list of CALL statement |
| $ | Only if user data to be stored |
(1) The meaning of this field depends on the value
specified for "Call Type". See Calling Adabas, The Control
Block for details.
(2) only if the multifetch
feature is used
ET
Adabas returns in this field the sequence number for the transaction. This number is provided in binary format.
Transaction sequence numbers are assigned in ascending sequence during a given user session, starting with 1. The value 0 will be returned if the transaction has performed no updates.
Adabas returns the response code for the command in this field. Response code 0 indicates that the command was executed successfully.
If user data is to be stored in an Adabas system file, the number of bytes of user data to be stored must be specified in this field.
Adabas will store the number of bytes specified in this field. The maximum number of bytes which may be specified is 2000 bytes.
If no user data is to be stored, this field is not used.
The ISN buffer length (in bytes). This buffer is only used in conjunction with the Multifetch feature. The value specified may not be smaller than 4 + (number of ISNs * 8), otherwise the Multifetch feature will be ignored.
If this field is set to ‘S’, an end of subtransaction is performed, otherwise an end of a logical transaction is performed. If this field is blank, all records in hold for the current transaction are released. If the field is set to `M', only the ISNs specified in the ISN Buffer are released from hold. to Programming Considerations, Multifetch Feature for more detailed information.
If this field is set to ‘T’, the ET command releases all resources that are in use for the current user session: it is equivalent to (but more efficient than) a CL command followed by an OP command with the Record Buffer set to ‘.’ and command option 1 set to the same value as in the previous OP command.
Note:
The ‘T’ option has been introduced for use after an OP without the
‘R’ option. If you perform an ET command with the ‘T’ option after an OP
command with the ‘R’ option, all subsequent commands that access any file will
get a response code 17. This is because using the ‘T’ option for the ET command
by mistake does not allow access to other files that are not already in the
file list.
An `E' in this field indicates that user data is to be stored in an Adabas system file.
If this field is set to ‘H’, all locked records remain in hold status, but exclusive locks are downgraded to shared locks.
For some response codes, Adabas returns detailed information in this field. See Adabas Messages and Codes for further information.
The user data to be stored in an Adabas system file is provided in this buffer.
The data will be retained until the user issues the next ET or CL command in which ET data is provided. The user data will be retained when the user session terminates only if the user issued an OP command in which a non-blank USERID was provided.
The user data can be in any format and Adabas performs no conversion on it.
This buffer contains the ISNs and file numbers that are to be unlocked. This buffer is only used in conjunction with the Multifetch feature. If no records are to be unlocked, the first 4 bytes of this buffer must be set to zeros.
For a detailed layout description of the ISN buffer, see Programming Considerations, Using the Multifetch Feature (Transaction Control).
Command Code ET
Command Option 2 b (blank; no user data is to be stored)
Command Code ET
Record Buffer Length 25 (25 bytes of user data to be stored)
Command Option 2 E (user data to be stored)
Record Buffer User Data For Transaction